How To Configure AWS Direct Connect.
AWS Direct Connect is a high-speed, low-latency connection that allows you to access public and private AWS Cloud services from your local (on-premises) infrastructure.
The connection is enabled via dedicated lines and bypasses the public Internet to help reduce network unpredictability and congestion. This can give us some significance and advantages in terms of bandwidth as well as latency. And it ensures that we have got a consistence network for use. It will cost more than if you establish an AWS-managed VPN across the Internet.
Let’s look at the configuration of Direct Connect.
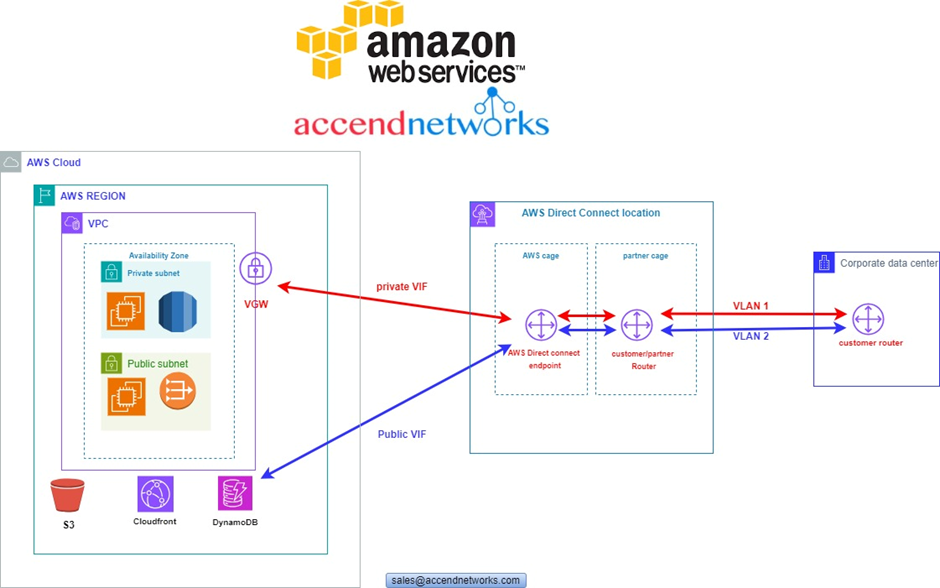
According to our reference architecture above, we have an AWS region with A VPC, and we’ve got a corporate data Center that could be an office. What we want to do is to connect that corporate data center to AWS.
To do that, we have to connect that via what is called an AWS direct connect location and this can be found in many cities around the world.
In the direct connect location, there is something called an AWS cage, and that’s where AWS has its networking equipment.
And then there is a customer or a partner cage, customer means that you will also own a rack into that Data Center with your networking equipment.
A partner simply means an APN partner partnered with AWS, and they have their cage of networking equipment and you can get a connection into their cage, and they do the connectivity into the AWS.
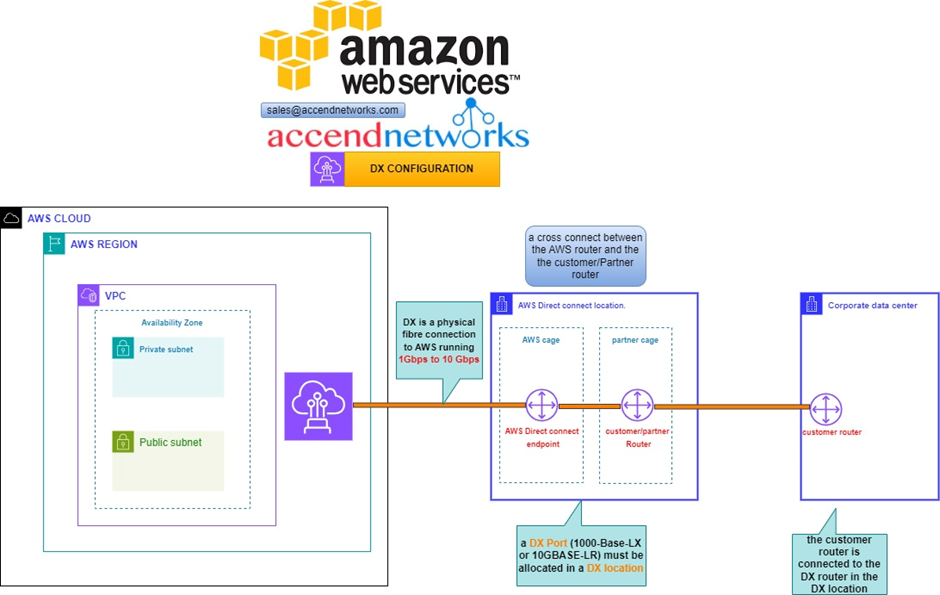
So, the way it works is that there are routers into these cages, into the direct connect location. Then a DX port (Direct connect port) must be allocated, in the Direct connect location. So, this is the port into which you are going to plug into a cross-connect.
The cross-connect is a cable that goes between the customer or partner cage, into the DX port that has been allocated into the AWS cage.
We then have a customer router in the corporate Data Center and we need to connect that to the DX router in the Direct Connect location. So that’s where we form the entrance connection.
So, AWS has their connection from their cage into the direct connect in the region but you must connect from your corporate data Center to the customer partner cage.
This is where some expenses and some challenges may take place because you will find you need to connect from your Data Center to the customer cage location if you don’t have a pre-existing location and sometimes that connection takes a bit of money and might take quite a bit of time.
It’s something you cannot set up very quickly, with Direct Connect, it takes weeks to months. And that’s how long Direct Connect takes to provision.
The actual DX connection is a physical fiber connection to AWS and runs either 1Gps or 10Gps.
Key Benefits of Direct Connect.
Private connectivity between your AWS and data Center or office,
Consistency network experience means increased speed and lower latency/consistency.
It can lower the cost for organizations to transfer large volumes of Data.
Let’s look at a bit more details.
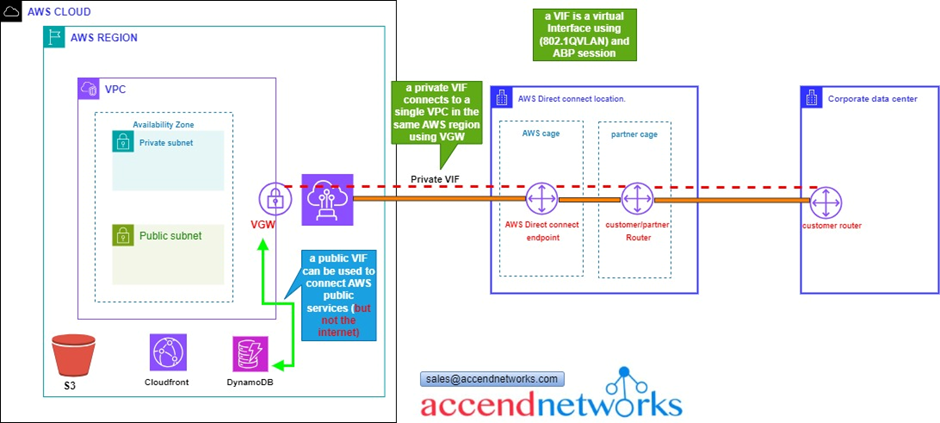
Once we have established a physical connection, we then have to establish something called a virtual interface. as shown above by our reference architecture.
There are public and private virtual interfaces.
A private virtual interface connects to a single VPC in the same AWS region using a virtual private gateway VGW.

A VIF is essentially a virtual interface that uses 802.1Q VLAN and BGP sessions.
NOTE: 802.1Q VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) are two distinct networking concepts.
The next Virtual interface is public, and what this does is to connect you to the AWS public services in any region. So, private VIF goes into the same region as the actual physical connection, but the public VIF can connect to a public service in any region. It doesn’t connect you to the Internet, so you can’t use it for internet purposes.
What if you have multiple VPCs in the region,
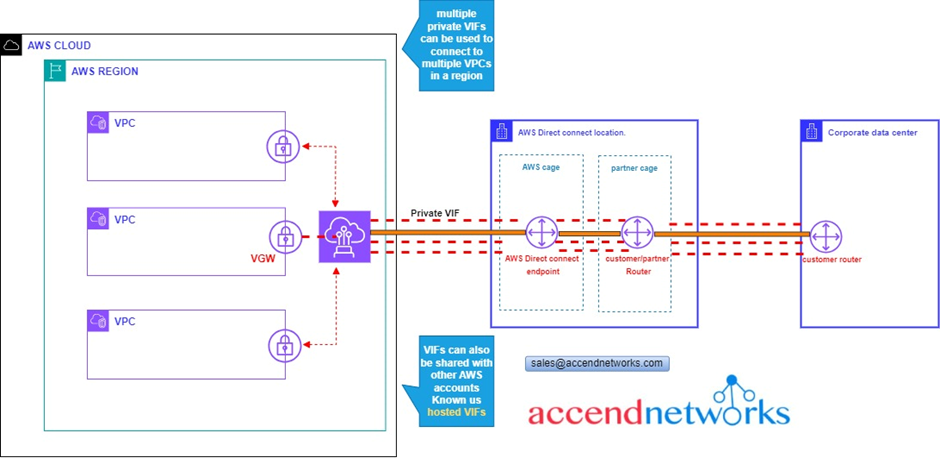
In this case, you will have multiple VGWs and multiple private VIFs that we will use to connect to those VGWs. So, you are connecting to multiple VPCs each is connected over a separate private face.
This can also be shared with other AWS accounts, when you do that, is known as a hosted VIF.
You can get speeds of 50Mbps to 100Mbps if you use an APN partner. An APN partner will have a connection already to AWS, and essentially, they are giving you a subset of that connection.
This can be implemented, either via a hosted, VIF, or a hosted connection.
Hosted VIF, is a single VIF, that is shared with other customers. In that case, there is a shared bandwidth.
Or you use a hosted connection, that is a DX with a single VIF dedicated to you, so obviously there is a cost implication to this, but if you go with the cheaper option, the hosted VIF, you are going to ensure that you understand that there is shared bandwidth happening there.
NOTE: DX connections are not encrypted hence this could be a security risk.
So, the question is what can we do to make sure our data is encrypted?
We can have an IPsec S2S VPN (site-to-site VPN connection) running over a VIF to add encryption in transit, so essentially you are running Direct Connect then on top of Direct Connect so you encrypt the traffic that goes over that direct connect using an AWS managed VPN connection.
Link aggregation groups (LAGs) can be used to combine multiple physical connections into a single logical connection and use LACP (the link aggregation control protocol). This is just for improved speed; it’s not going to give you high availability.
DX design for high availability.
On the subject of high availability, let’s look at how you can design DX to make sure that you have high availability built into these connections. When we look at our first architectural diagram, we can identify very many points of failure. For high Resiliency for critical workloads using two single connections to more than one location. The below design helps to prevent connection against device, connectivity, and complete location failure.
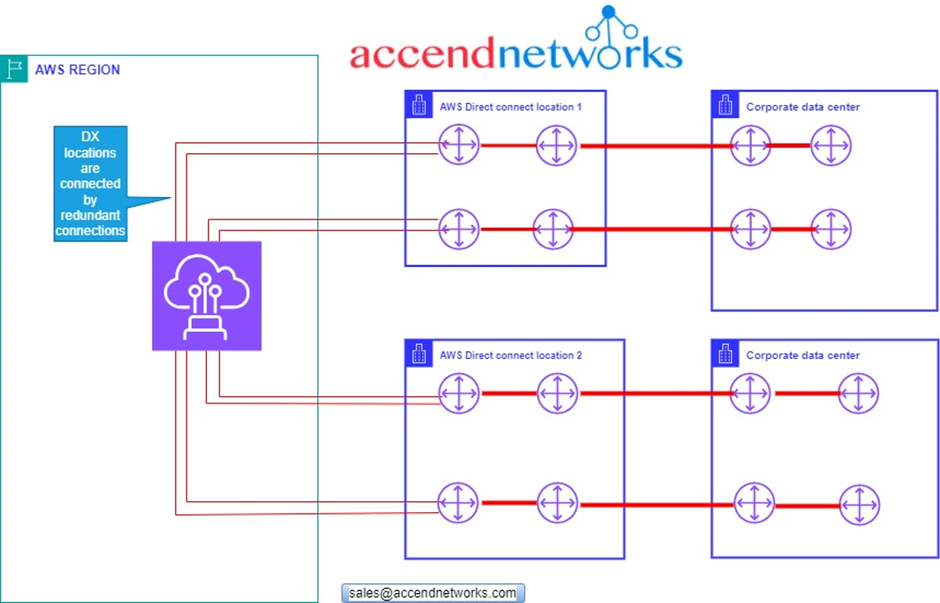
This is going to be a considerably more expensive setup than if we have very low levels of redundancy. As you add redundancy you always add cost but you have to consider your business and the impact of an outage.
another implementation we could do to add redundancy is rather than adding a Direct Connect connection, we can add an IPsec VPN as shown below.
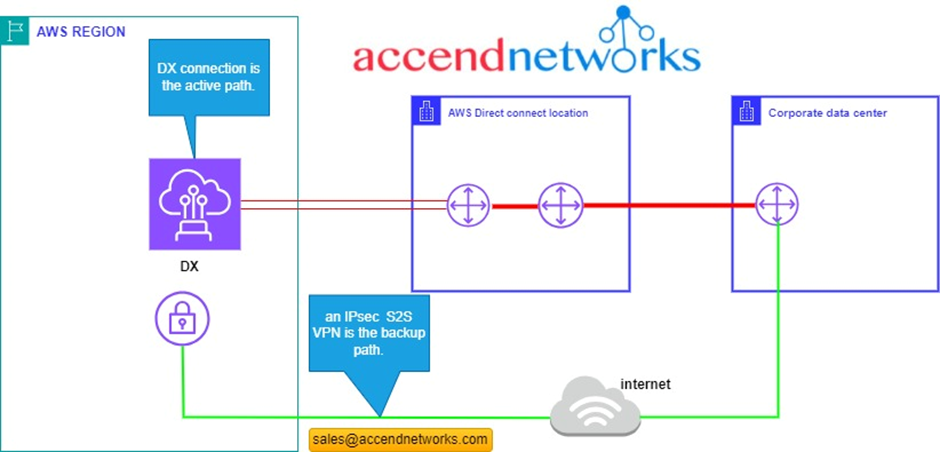
In this architecture we have the DX connection which is the primary path, we have a VGW which is connected back to the corporate data Center using a site-to-site VPN, which is the backup path, we give priority to our traffic to use the DX link, but if the DX link fails due to some reason, we have a backup path over the internet. but since the internet has some disadvantages, like lower bandwidth and considerably lower latency this might have an impact on your business. so, you get to consider an option that is best for your business but the last option could be significantly cheaper than having a fully redundant DX configuration.
a recommendation from AWS is that you should not use this architecture if your speeds are over 1Gbps. so, if you need more than 1Gbps of bandwidth don’t use this setup because of limitations in the AWS VPN.
This brings us to the end of this blog. Thanks for your attention.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at [email protected].
Thank you!.
