How To Create Serverless Computing with AWS Lambda.

In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, AWS Lambda has emerged as a revolutionary service, paving the way for serverless computing. This paradigm shift allows developers to focus on building and deploying applications without the burden of managing servers.
What is Lambda
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers.
Lambda runs your code on a high-availability compute infrastructure and performs all of the administration of the compute resources, including server and operating system maintenance, capacity provisioning automatic scaling, and logging. With Lambda, all you need to do is supply your code in one of the language runtimes that Lambda supports.
You organize your code into Lambda functions. The Lambda service runs your function only when needed and scales automatically. You only pay for the compute time that you consume — there is no charge when your code is not running.
Things That Can Cause Lambda Capabilities
AWS source triggers (DynamoDB functions, S3 situations, Message Queue functions, and so on)
AWS endpoints (Relaxation calls)
AWS endpoints (Relaxation calls)
Key Features of AWS Lambda:
Event-driven: AWS Lambda is designed to respond to events from various AWS services or custom events e.g. changes to data in an Amazon S3 bucket, updates to a DynamoDB table, etc.
Multiple Programming Languages: Lambda supports multiple programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, Go, Ruby, and .NET Core.
Automatic Scaling: Lambda automatically scales based on the number of incoming requests.
Cost-Efficient: AWS Lambda follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model. You are charged only for the compute time consumed by your code.
Built-in Fault Tolerance: AWS Lambda provides built-in fault tolerance by automatically distributing the execution of functions across multiple availability zones.
Use Cases for AWS Lambda:
Real-time File Processing: AWS Lambda can be used to process files uploaded to an S3 bucket in real-time.
Microservices Architecture: Lambda functions are well-suited for building microservices, allowing developers to break down large applications into smaller, manageable components promoting agility and maintainability.
API Backend: With the help of API Gateway, AWS Lambda can be used to build scalable and cost-effective API backends. This allows developers to focus on building the application’s logic without worrying about managing servers.
Data Transformation and Analysis: Lambda functions can process and analyze data from various sources, providing a serverless solution for tasks like log processing, data transformation, and real-time analytics.
Create a Lambda function with the console
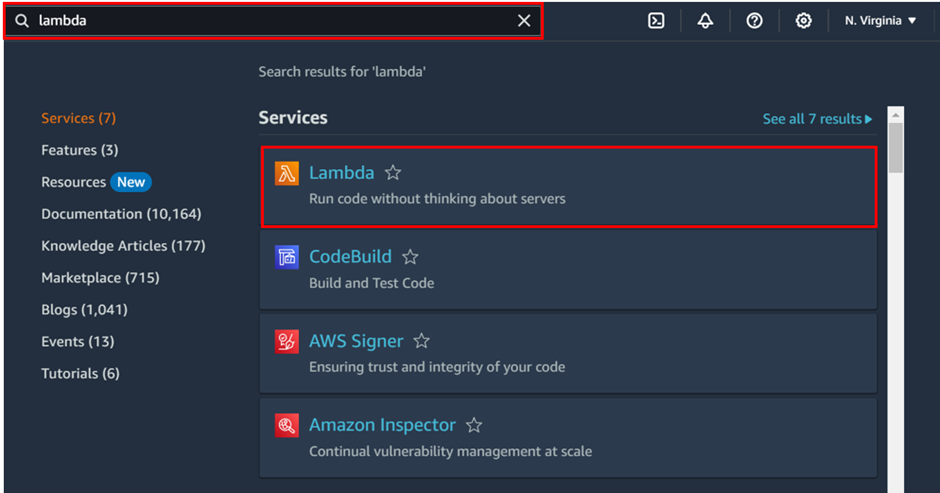
Log into the management console and type lambda in the search box then select lambda under services.
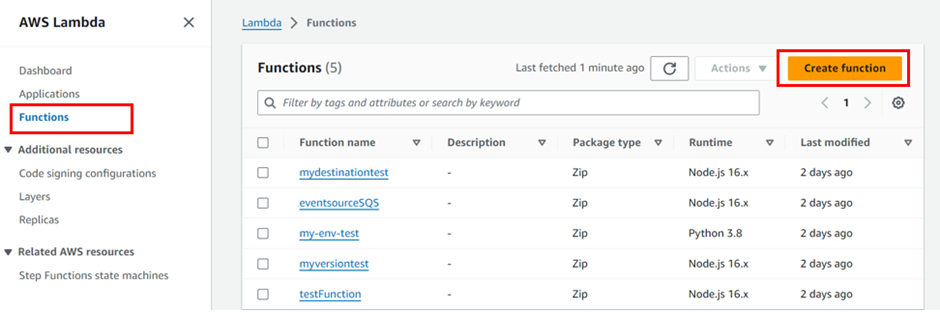
In the lambda dashboard on the left side of the navigation pane, select function then click create function.
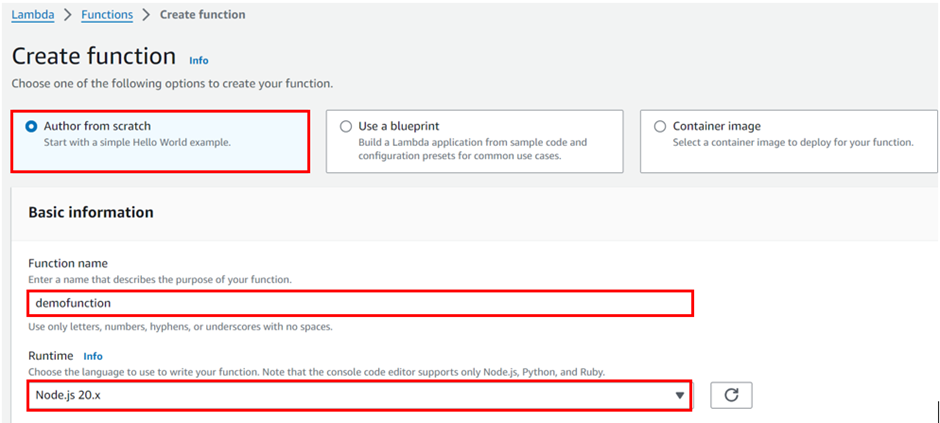
In the create function dashboard, Select Author from scratch then in the Basic information pane, for Function name enter mytestfunction.
Then for Runtime, choose Node.js 20.x
Then scroll down, leave the architecture set to x86_64, and choose the Create function.
Then for Runtime, choose Node.js 20.x
Then scroll down, leave the architecture set to x86_64, and choose the Create function.
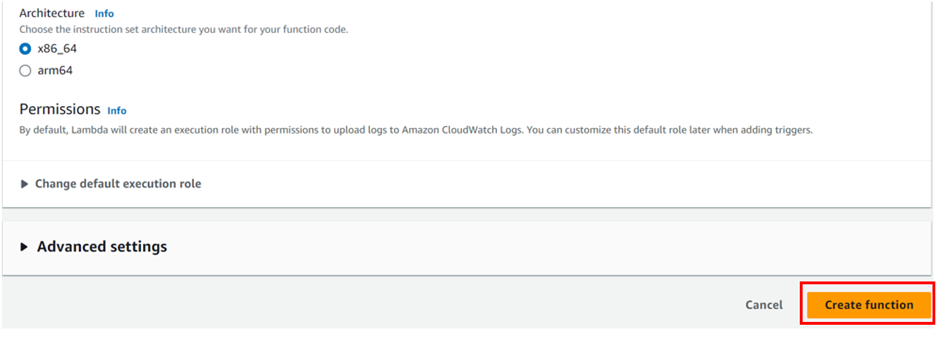
Remember default, Lambda will create an execution role with permissions to upload logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
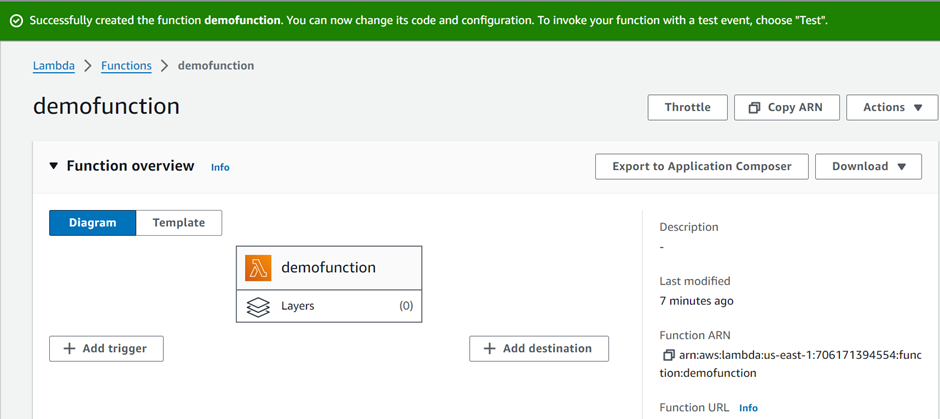
These are the only settings we need to create our function so scroll down and click create function.
Lambda creates a function that returns the message Hello from Lambda!
Lambda creates a function that returns the message Lambda also creates an execution role for your function. An execution role is an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role that grants a Lambda function permission to access AWS services and resources.
To see the role scroll down and select the configuration tab then select permission, in the execution role under the role name you can see the role.
Lambda creates a function that returns the message Hello from Lambda!
Lambda creates a function that returns the message Lambda also creates an execution role for your function. An execution role is an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role that grants a Lambda function permission to access AWS services and resources.
To see the role scroll down and select the configuration tab then select permission, in the execution role under the role name you can see the role.
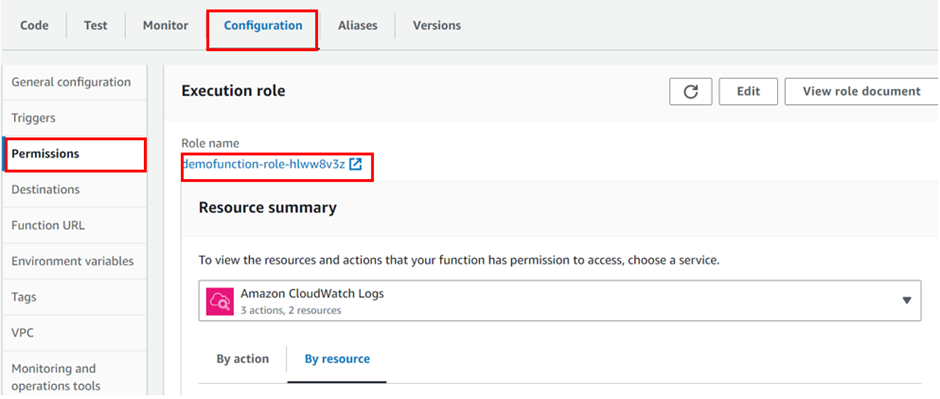
When you select it, it will take you to the I am console and you can see the policy.
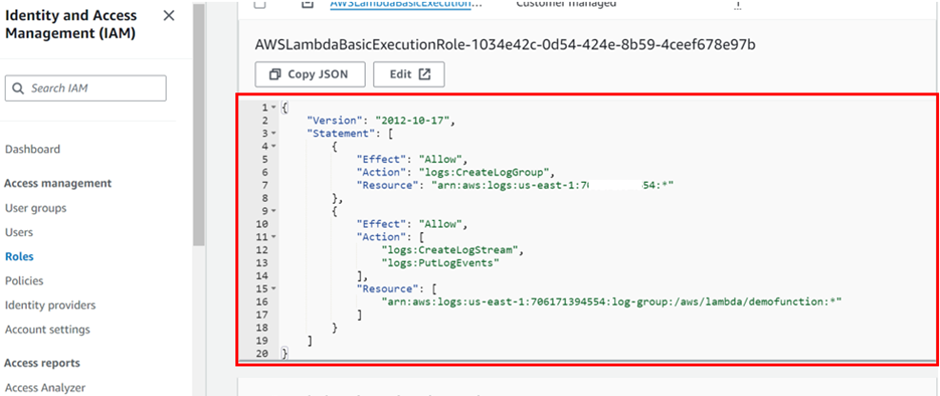
Now back to lambda under code, we can see the Hello from Lambda! Code.
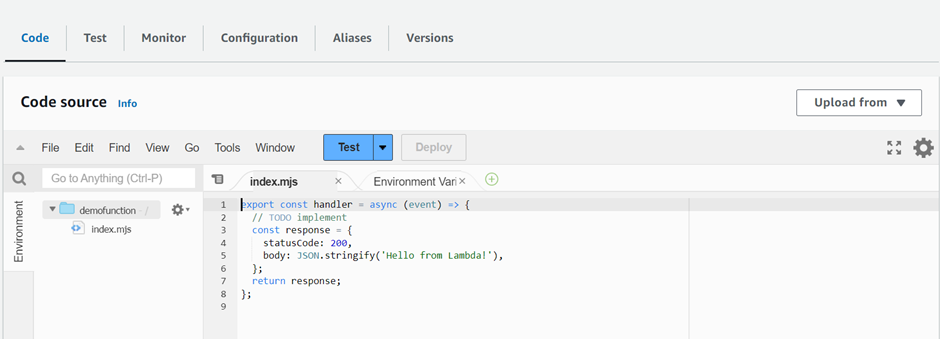
We will change this code with a different code Choose the Code tab.
In the console’s built-in code editor, you should see the function code that Lambda created. Then we will replace this cord with our code as shown below.
In the console’s built-in code editor, you should see the function code that Lambda created. Then we will replace this cord with our code as shown below.
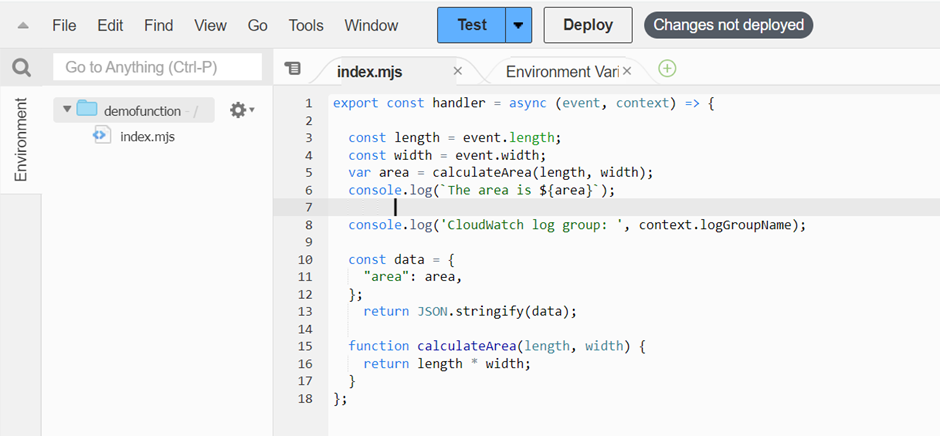
Select Deploy to update your function’s code. When Lambda has deployed the changes, the console displays a banner letting you know that it’s successfully updated your function.
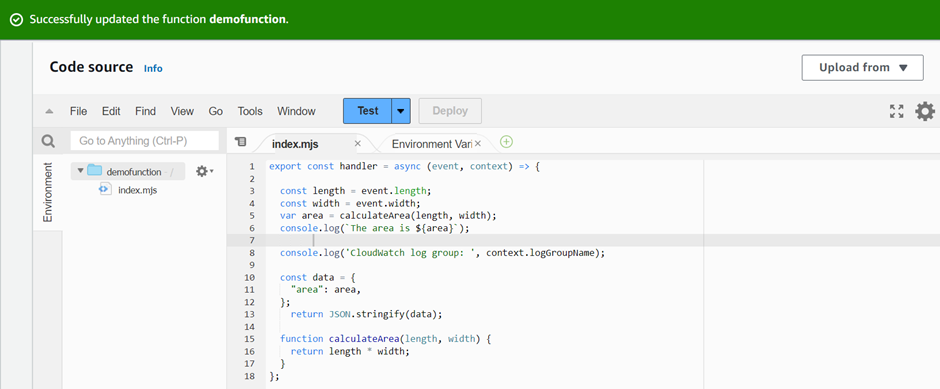
Invoke the Lambda function using the console.
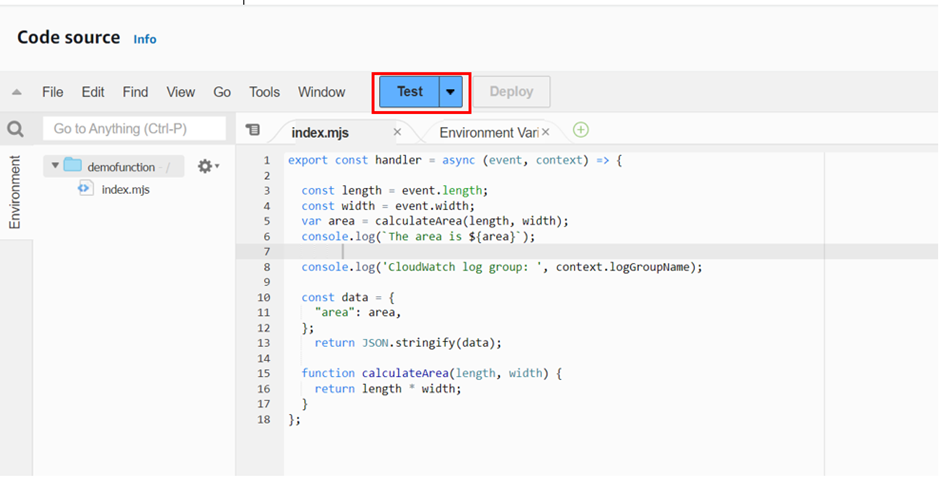
To invoke our lambda function using the Lambda console, we first create a test event to send to our function. The event is a JSON-formatted document.
To create the test event
In the Code source pane, we will choose Test then you will be taken to configure the test console.
select Create new Event, then for Event name enter myTestEvent In the Event JSON panel, we will paste in our code as shown below. Then we choose to save.
To create the test event
In the Code source pane, we will choose Test then you will be taken to configure the test console.
select Create new Event, then for Event name enter myTestEvent In the Event JSON panel, we will paste in our code as shown below. Then we choose to save.
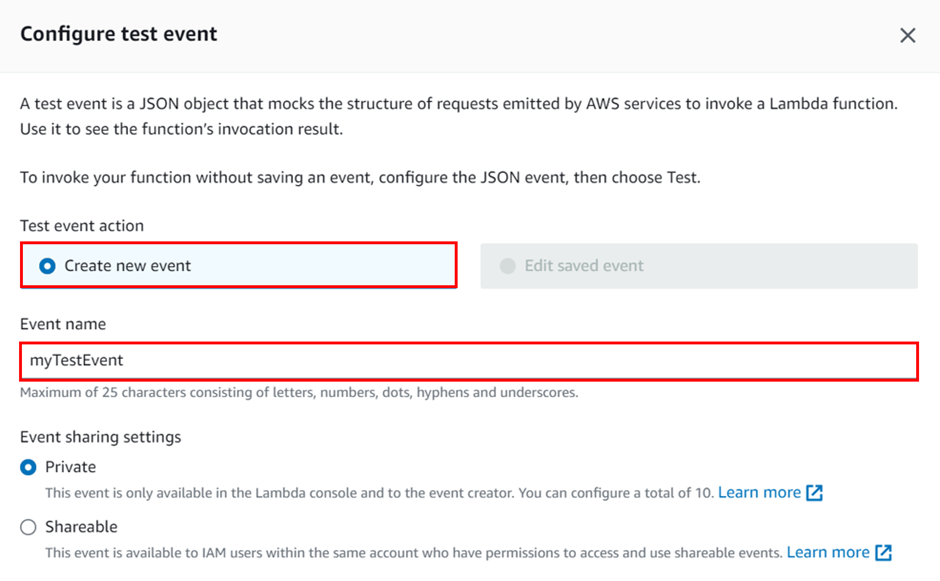
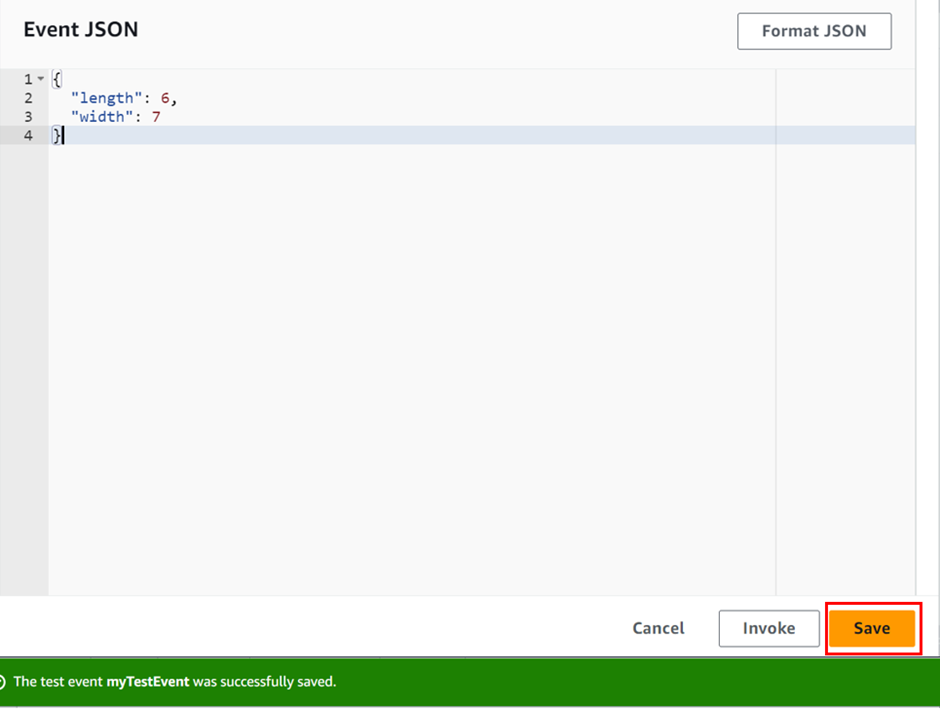
We will now test our function and use the Lambda console and CloudWatch Logs to view records of our function’s invocation.
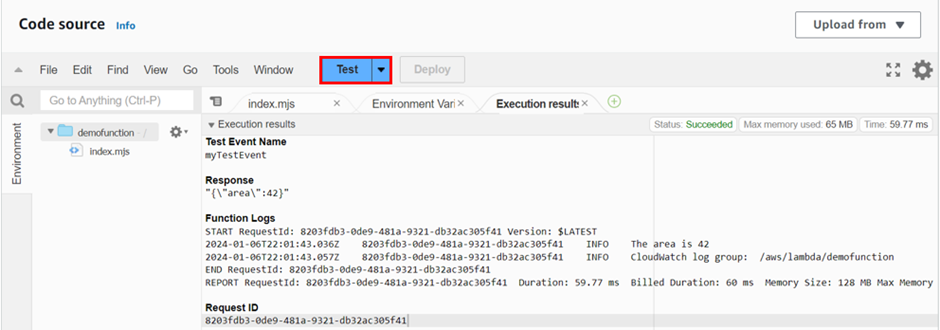
To test our function, In the Code source pane, we will choose Test. Then wait for our function to finish running. We will see the response and function logs displayed in the Execution results tab as shown below. This confirms that our lambda function was invoked successfully.
To test our function, In the Code source pane, we will choose Test. Then wait for our function to finish running. We will see the response and function logs displayed in the Execution results tab as shown below. This confirms that our lambda function was invoked successfully.
This brings us to the end of this blog.
Pull down and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at [email protected].
Thank you!
Pull down and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at [email protected].
Thank you!
