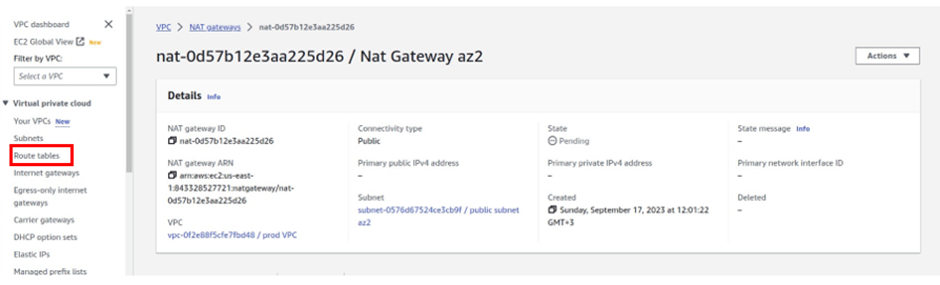
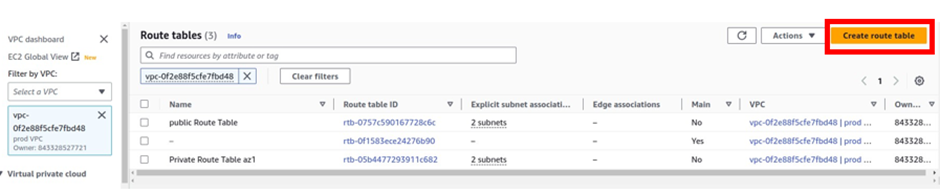
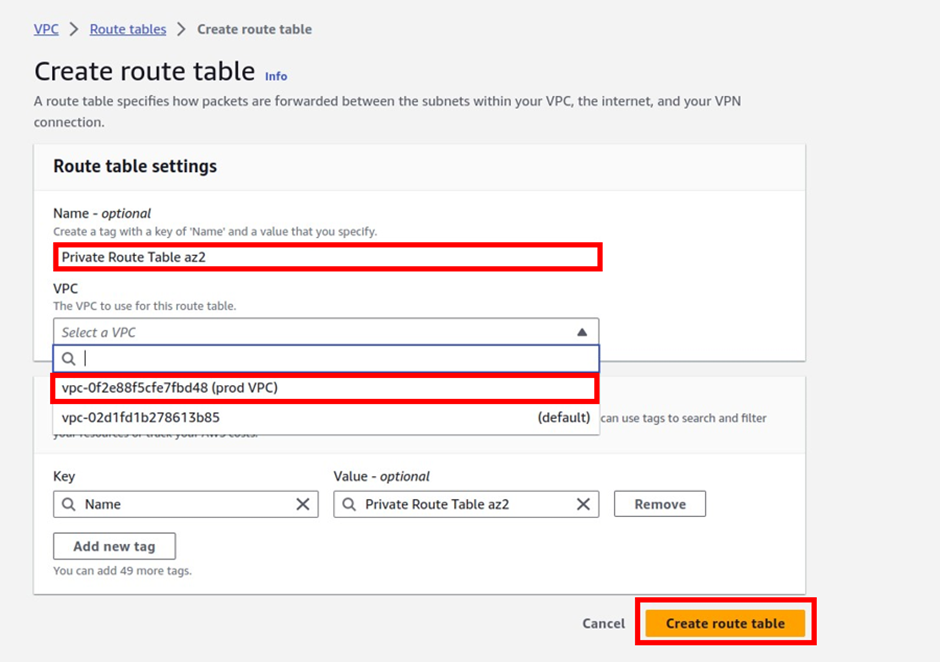
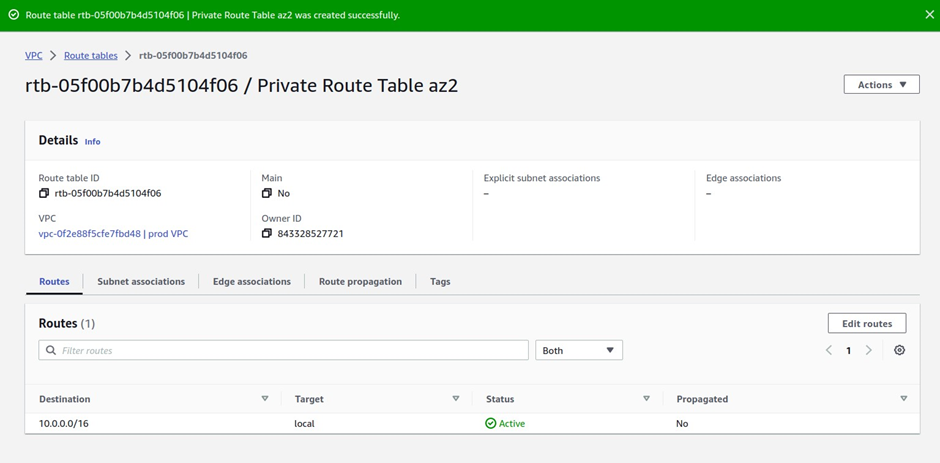
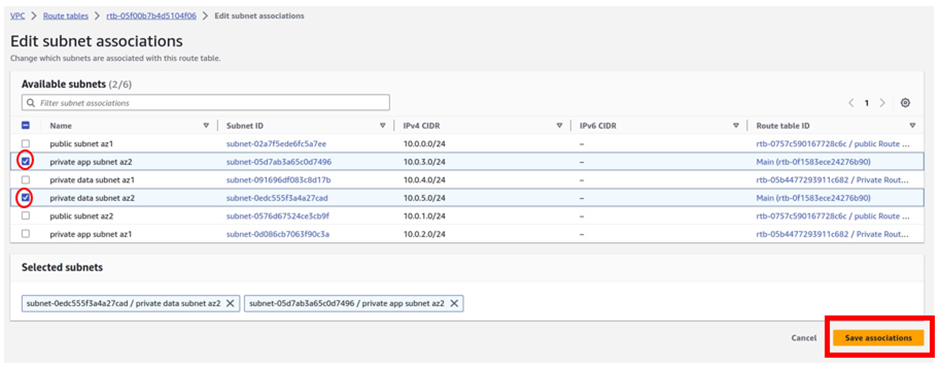
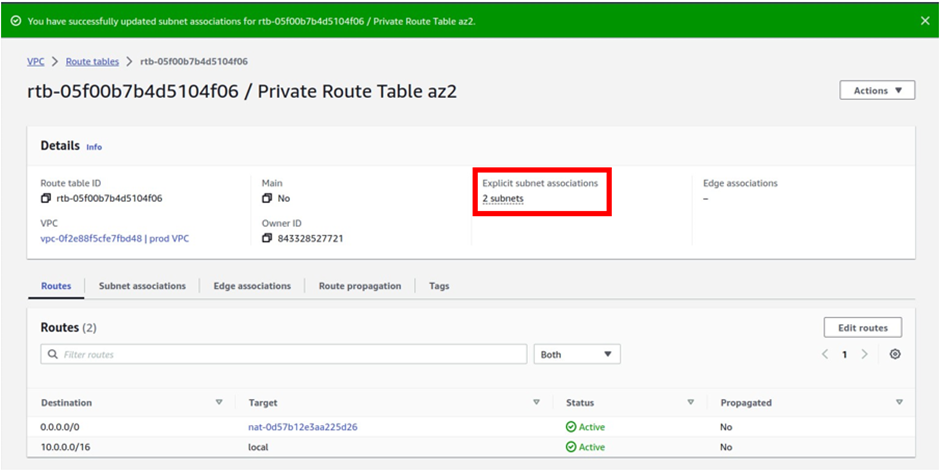
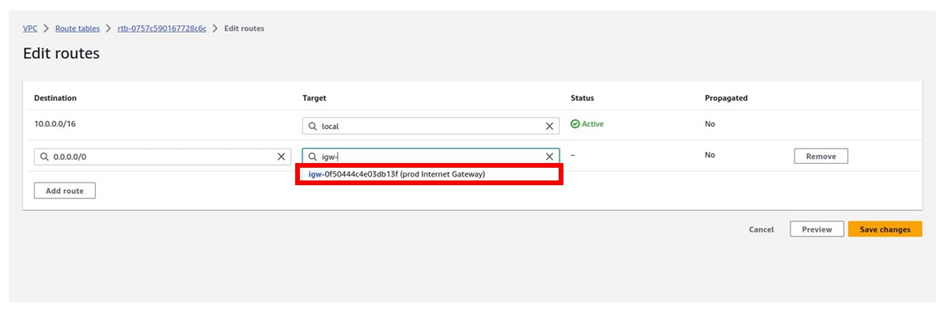
How Does Amazon CloudWatch Work?

Amazon CloudWatch monitors your Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources and the applications you run on AWS. Additionally, CloudWatch enables real-time monitoring of various AWS resources including EC2 instances, RDS database instances, load balancers, and AWS Lambda. CloudWatch allows to collect & track metrics, monitor log files, set alarms, and automate reactions to AWS resource changes.
It automatically provides metrics for CPU utilization, latency, and request counts. Moreover, it can monitor other vital metrics such as memory usage, error rates, etc.
CloudWatch Metrics
CloudWatch metrics give the users visibility into resource utilization, application performance, and operational health. These help you make sure that you can resolve technical issues and streamline processes and that the application runs smoothly.
How does Amazon CloudWatch work?
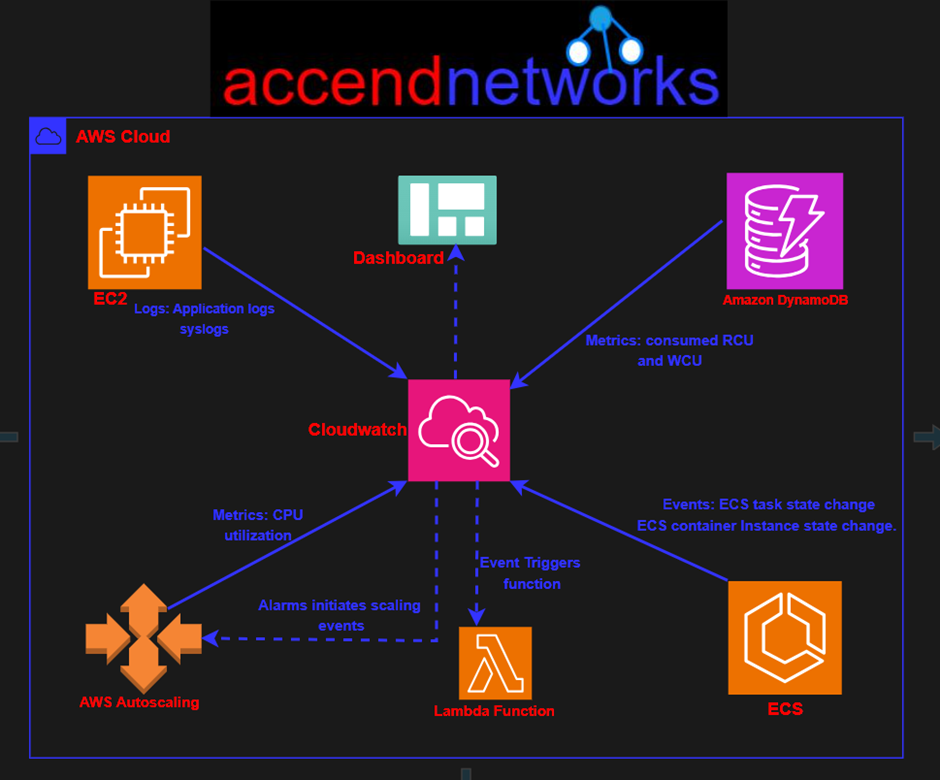
Basically, the Amazon CloudWatch primarily performs the following four actions:
Collect metrics and logs
In the first step, CloudWatch gathers metrics and logs from all your AWS services, like AWS EC2 instances. Following this, CloudWatch retrieves these metrics from the repository. This repository may also contain custom metrics entered into it.
Monitor and visualize the data
Next, CloudWatch monitors and visualizes this data using CloudWatch dashboards. These dashboards provide a unified view of all your AWS applications, resources, and services, on-premise or in the cloud. In addition, you can correlate metrics and logs. Consequently, this facilitates visual analysis of your resources’ health and performance.
Act on an automated response to any changes.
In this step, CloudWatch executes an automated response to any operational changes using alarms. For example, you can configure an alarm to start or terminate an EC2 instance after it meets specific conditions. Additionally, you can use alarms to start services such as Amazon EC2 auto-scaling or Amazon SNS
If a triggered alarm activates, you can set up automated actions such as auto-scaling.
Analyze your metrics
The final step is analyzing and visualizing your collected metric and log data for better insight. You can perform real-time analysis using CloudWatch Metric Math which helps you dive deeper into your data.
Amazon CloudWatch Logs
CloudWatch Logs helps users access, monitor, and store access log files from EC2 instances, CloudTrail, Lambda functions, and other sources. With the help of CloudWatch Logs, you can troubleshoot your systems and applications. It offers near real-time monitoring and users can search for specific phrases, values, or patterns. You can provision CloudWatch logs as a managed service without any extra purchases from within your AWS accounts. CloudWatch logs are easy to work with from the AWS console or the AWS CLI. They have deep integration with AWS services. Furthermore, CloudWatch logs can trigger alerts based on certain logs occurring in the logs.
For log collection, AWS provides both a new unified CloudWatch agent and an older CloudWatch Logs agent. However, AWS recommends using the unified CloudWatch agent. When you install a CloudWatch Logs agent on an EC2 instance, it automatically creates a log group. Alternatively, you can create a log group directly from the AWS console.
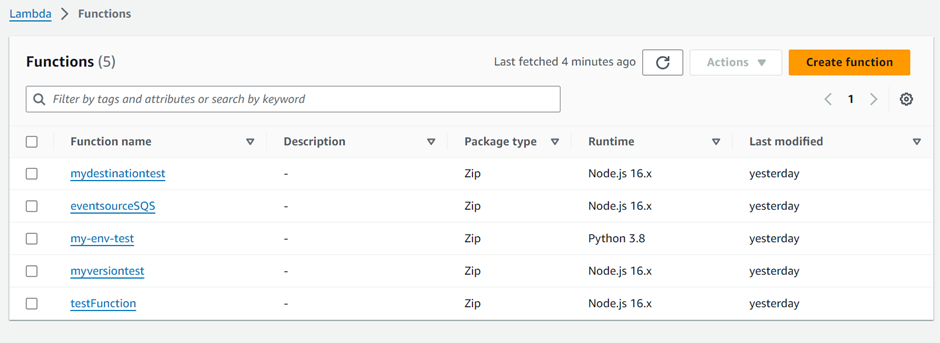
For the demonstration, I have the following Lambda functions that I created.
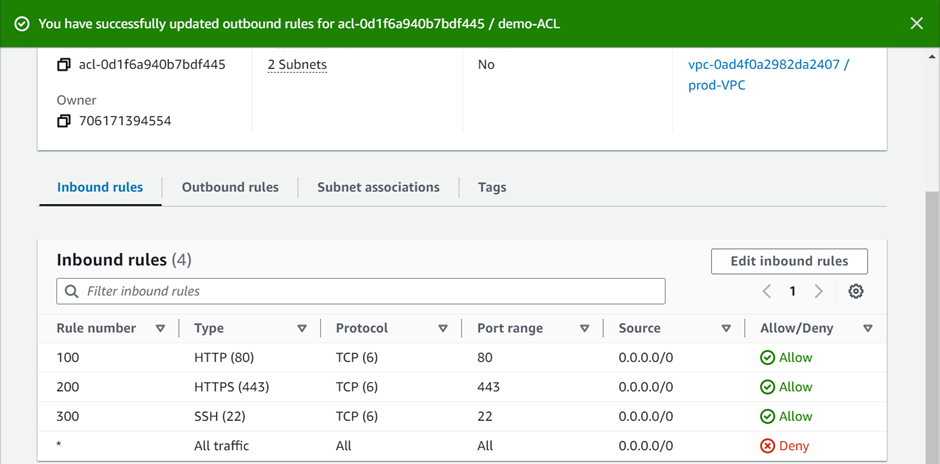
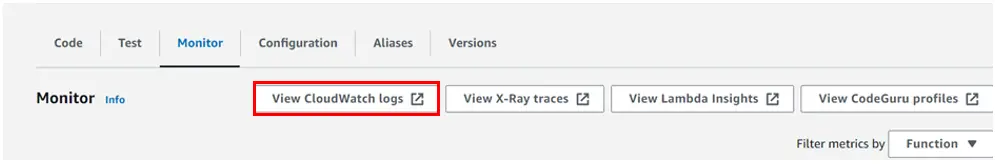
Next, we will proceed to view the CloudWatch logs of my destination test function. To do so, select it and navigate to the monitoring tab. Then, click on “View CloudWatch logs,” as shown below.
After clicking “View CloudWatch logs,” the system takes you to the CloudWatch dashboard. And under log streams, you can select one of the log streams to view.
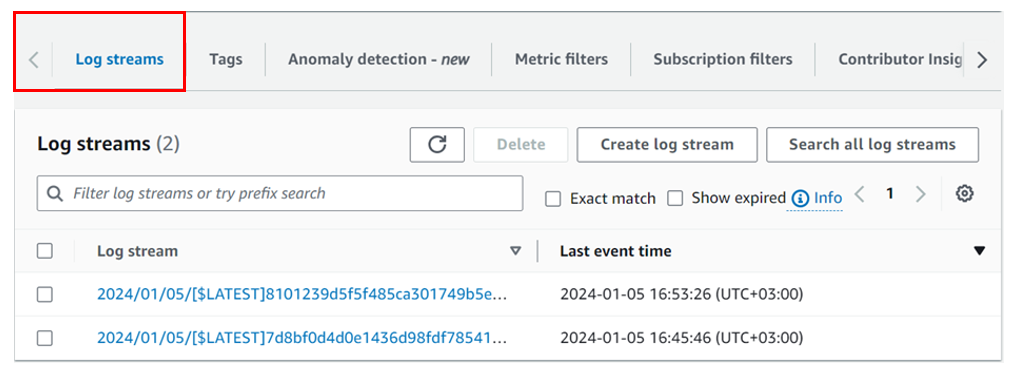
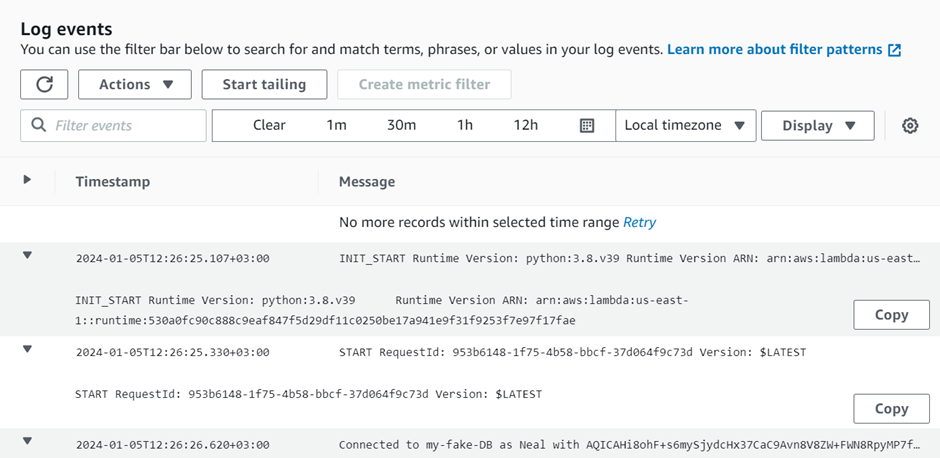
On selecting the first one we can see the below logs events.
CloudWatch Events
CloudWatch Events allows users to consume a near real-time stream of events as changes to their AWS environment occur. These event changes can subsequently trigger notifications or other actions. Despite this, CloudWatch events monitor EC2 instance launches, shutdowns, and detect auto-scale events. Additionally, it detects when AWS services provision or terminate.
What are the benefits of Amazon CloudWatch?
Access all monitoring data from a single dashboard
Essentially, Amazon CloudWatch allows you to monitor data from different services using a single dashboard.
Collects and analyzes metrics from AWS and on-premise applications
Thanks to its seamless integration with over 70 AWS services, CloudWatch can collect and publish metric data automatically.
Using this metric and log data, you can now optimize your AWS services and resources
Using this metric and log data, you can now optimize your AWS services and resources
Improve your operational efficiency and optimize your available resource
The Amazon CloudWatch service provides real-time insights into cloud operations. Hence, this enable you to optimize operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Improve operational visibility
With the Amazon CloudWatch service, you gain operational visibility across all your running applications
Extract valuable insights
Ultimately, Amazon CloudWatch enables you to extract valuable and actionable insights from generated logs.
Conclusion
Using the Amazon CloudWatch service, you can monitor cloud-based applications and other AWS services. Consequently, this helps you in troubleshooting any performance issues. With its centralized dashboard, AWS administrators have complete visibility into applications and services across AWS regions.
In conclusion, this brings us to the end of this blog. Stay tuned for more.
For questions or AWS project assistance, contact us at [email protected]. or leave a comment below.
Thank you!