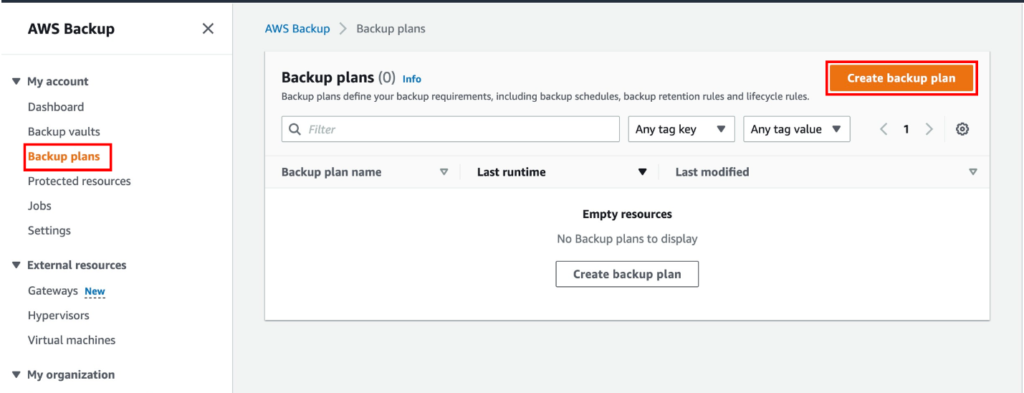
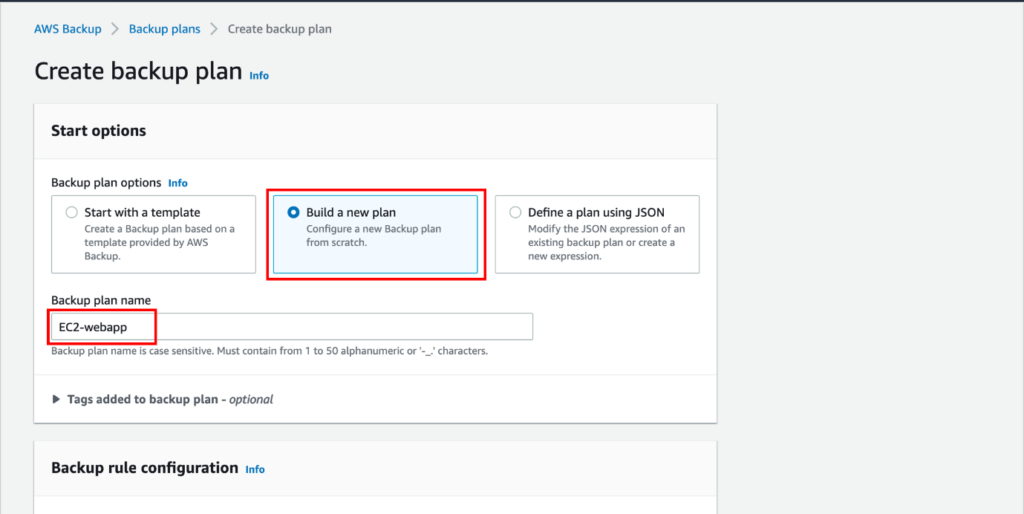
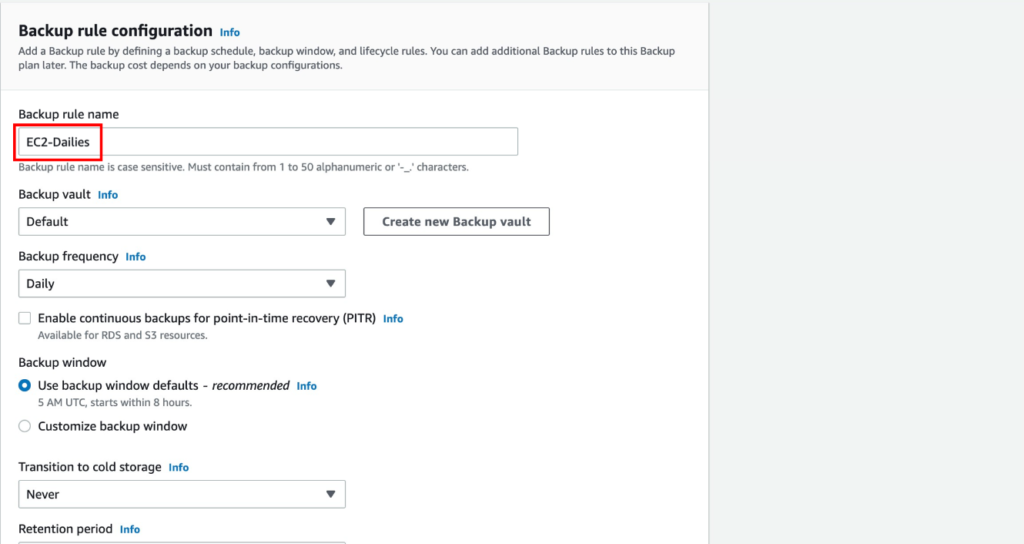
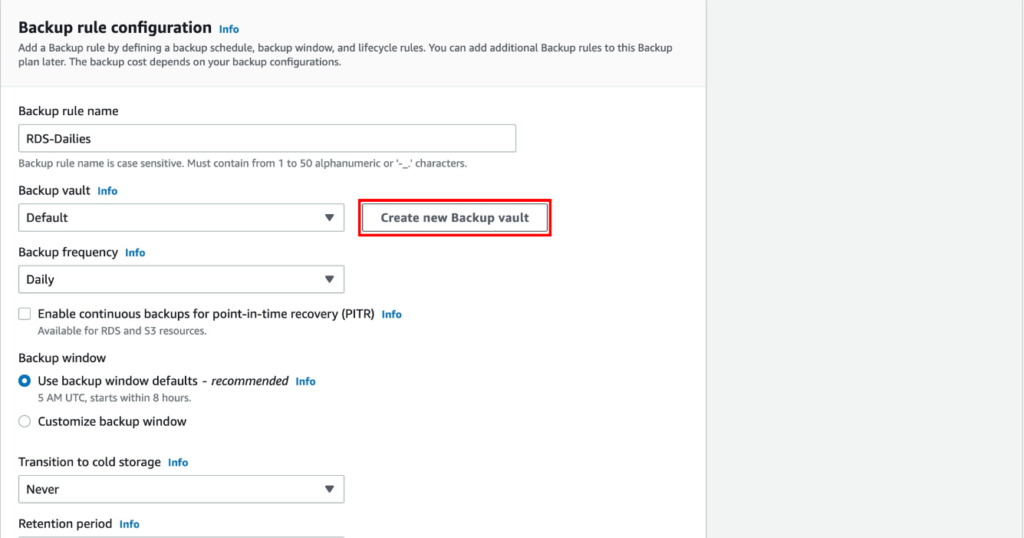
An Overview of DDoS Attacks: Understanding the Threat.
In the current digital era, cybersecurity is key. Among the various threats that organizations face are Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks which are particularly disruptive. DDoS attack defence is one of the top security concerns on the web today, regardless of the attacker’s purpose, because disruption of availability can result in financial losses and other undesirable repercussions. In this blog article we will explore how AWS Shield operates, its features, and its importance in the current cybersecurity landscape.
DDoS Attacks
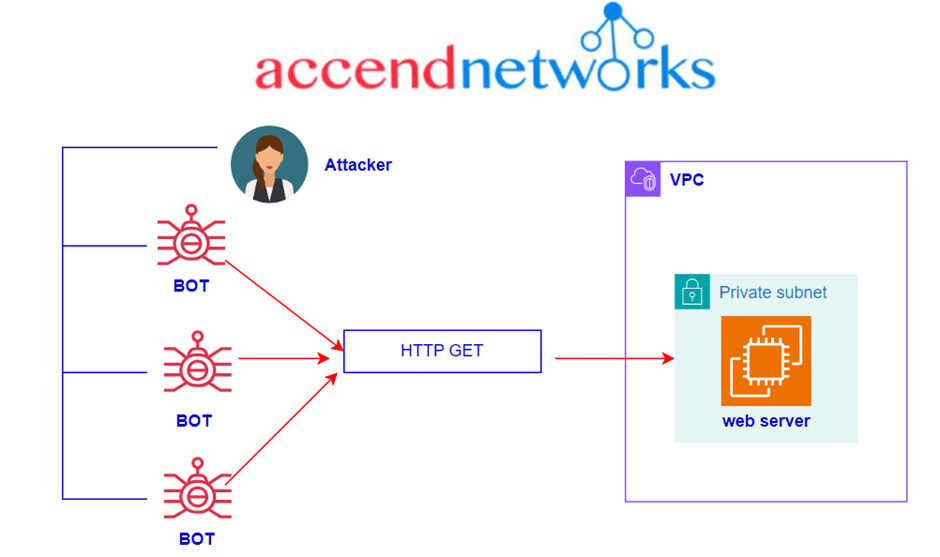
DDoS attacks involve overwhelming a server, service, or network with more traffic than it can handle, causing it to slow down or crash. Attackers use millions of tonnes of traffic to bring down a victim’s web applications from multiple sources, which is known as DDoS extortion.
There are basically 3 types of DDoS attacks:
Volume-Based Attacks
These attacks use methods to create huge amounts of traffic in order to completely saturate bandwidth, causing a traffic jam that prevents genuine traffic from flowing into or out of the targeted site.
Protocol Based Attacks
By consuming enormous amounts of per-connection resources, these attacks misuse stateful protocols and therefore put a strain on firewalls and load balancers.
Application Layer Attacks
Some of the most advanced DDoS attacks take use of flaws in the application layer by establishing connections and launching process and transaction requests that consume finite resources such as disc space and memory.
AWS Shield Overview
What is AWS Shield?
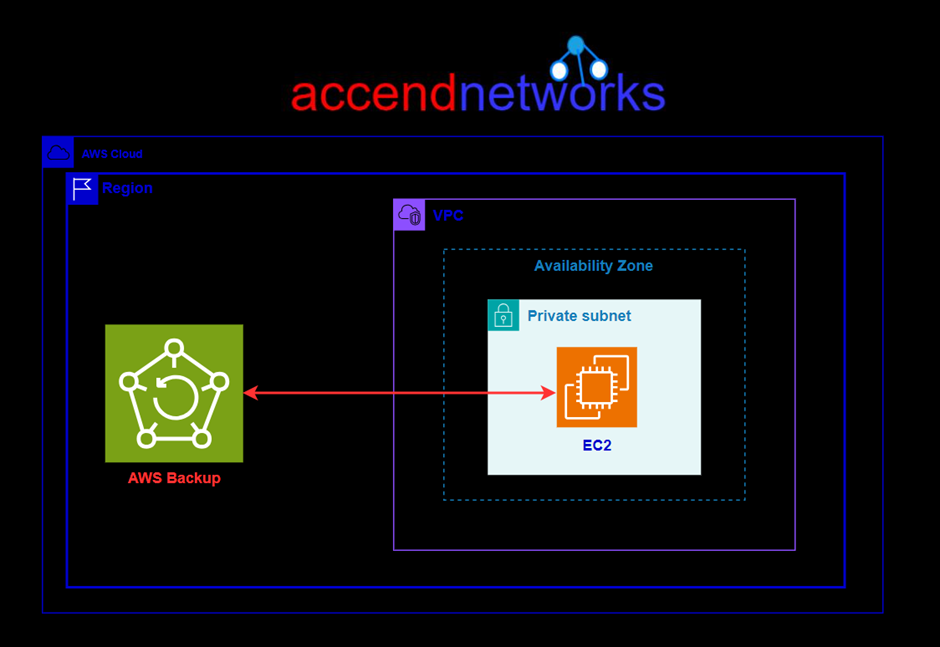
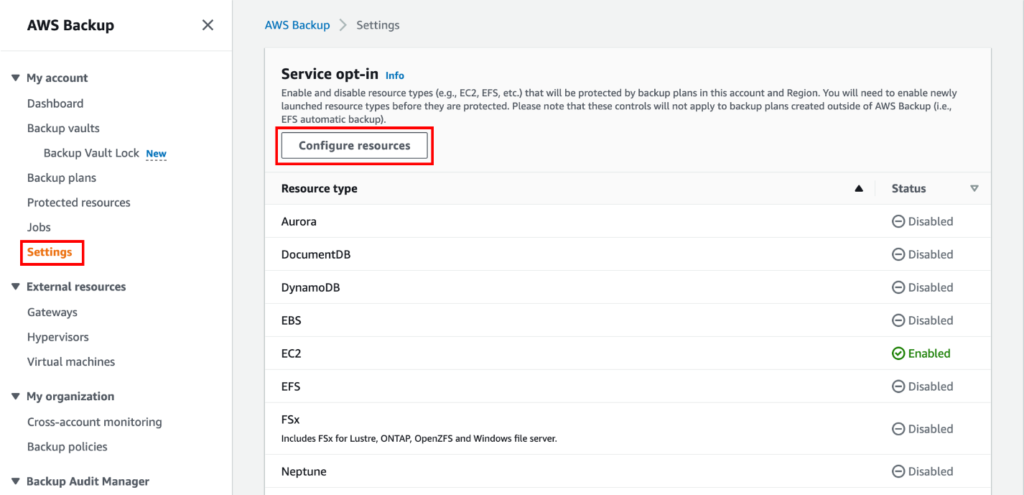
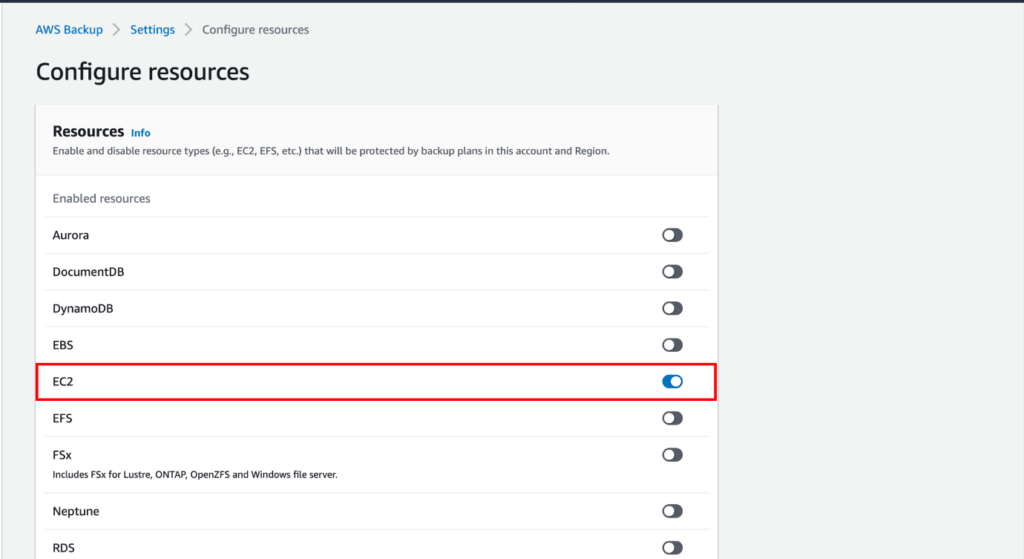
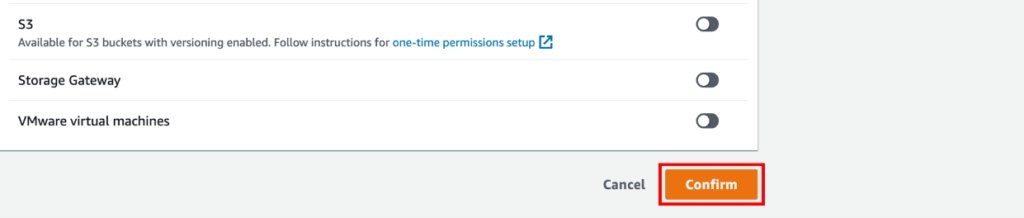
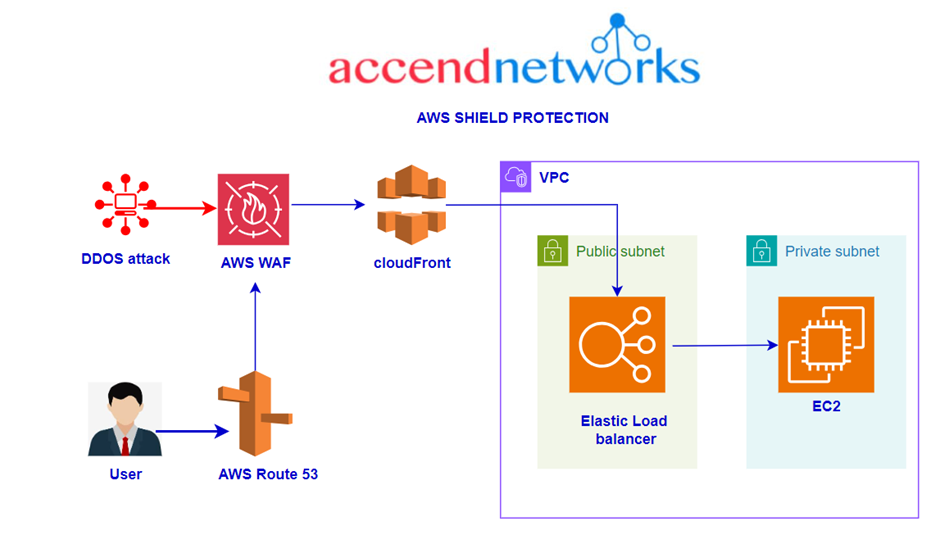
AWS Shield is a managed solution for preventing DDoS attacks basically on AWS-hosted applications. It inspects traffic in real-time and applies mitigation strategies automatically in order to avoid performance degradation.

There are basically two types of AWS Shields.
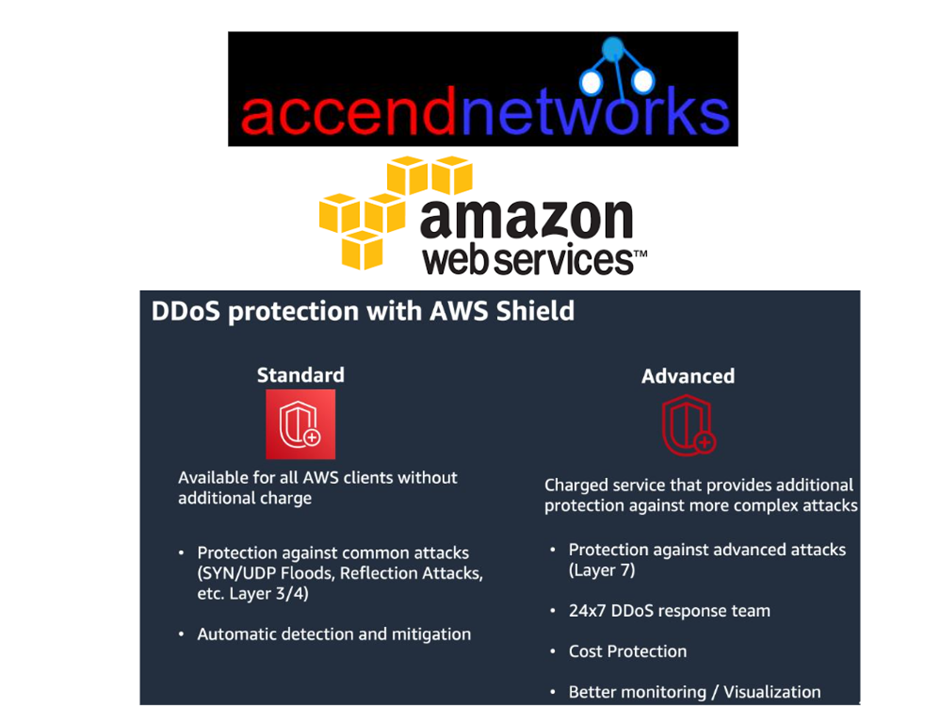
AWS Shield Standard (Free Service)
It is a free service offered to all AWS customers. It guards you against 96% of today’s most prevalent attacks, such as SYN/ACK floods, Reflection attacks, and HTTP slow reads. This protection is deployed to your Elastic Load Balancers, CloudFront distributions, and Route 53 resources automatically and transparently.
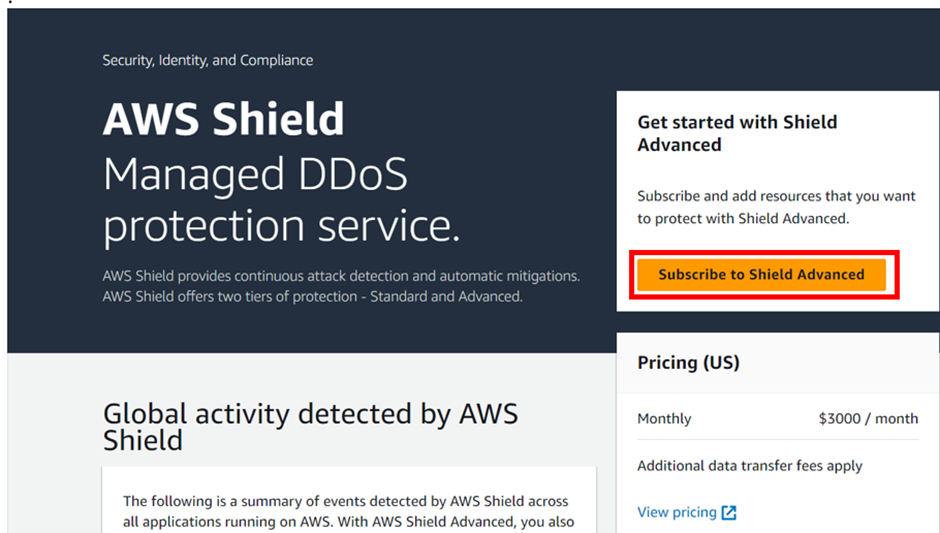
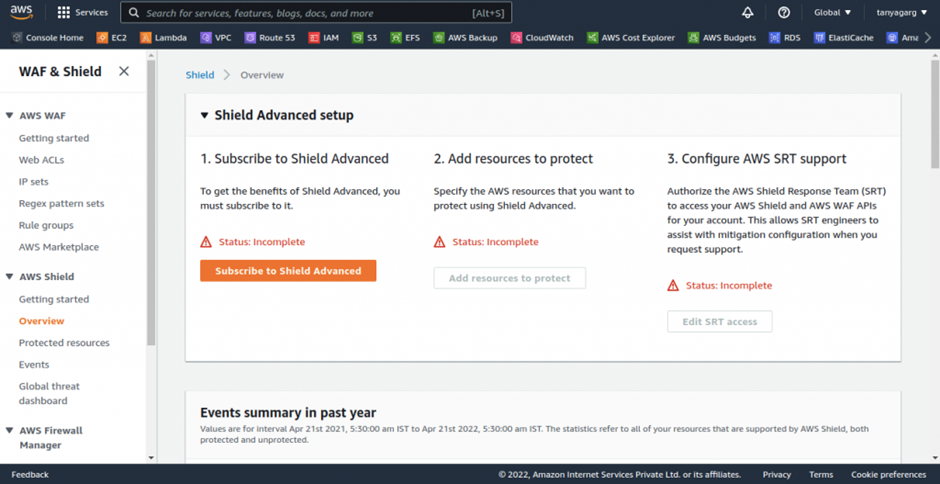
AWS Shield Advanced (Paid Service)
It is a paid service that adds volumetric DDoS mitigation, sophisticated attack detection, and mitigation for attacks at the application as well as network layers to AWS Shield.
You also have access to DDoS Response Team (DRT) 24*7 for tailored mitigation during attacks.
Key Features of AWS Shield.
Automatic Protection: AWS Shield offers automatic protection for all AWS customers at no additional cost. This basic protection, known as AWS Shield Standard, defends against most common, frequently occurring network and transport layer DDoS attacks.
Advanced Protection: AWS Shield Advanced provides enhanced protections for more sophisticated and larger scale DDoS attacks. It includes additional detection and mitigation capabilities, 24/7 access to the AWS DDoS Response Team (DRT), and financial protection against spikes in your AWS bill resulting from a DDoS attack.
Real-Time Visibility: AWS Shield Advanced customers have access to detailed attack diagnostics and the ability to create alarms in Amazon CloudWatch based on the occurrence of DDoS events.
Integration with AWS Services: AWS Shield works seamlessly with other AWS services like AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall), Amazon CloudFront, and Amazon Route 53, providing a holistic approach to security.
Why AWS Shield is Important
Comprehensive Protection
AWS Shield’s multi-layered defence strategy covers a wide range of attack vectors. Its integration with other AWS services ensures a robust security posture for your applications.
Cost-Effective
With its automatic protection feature, AWS Shield Standard offers fundamental DDoS protection at no extra cost, making it a cost-effective solution for all AWS customers. For those requiring advanced protection, AWS Shield Advanced offers additional benefits, including financial safeguards.
Reduced Complexity
Managing cybersecurity can be complex, AWS Shield’s managed service approach reduces this complexity, allowing organizations to focus more on their core business activities.
Enhanced Business Continuity
DDoS attacks can disrupt business operations significantly. AWS Shield enhances business continuity by ensuring that applications remain available and performant even under attack.
This brings us to the end of this blog, thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!