Scaling Big Data with Amazon Redshift: Insights into Managing Large Databases

In today’s world driven by data, companies face a flood of information making it essential to analyze and understand this data. This is where Amazon Redshift, a fully managed cloud data warehouse service, comes into play. Designed to handle large-scale data analytics and processing tasks. It helps businesses to gain deeper insights, faster query performance, and cost-effective scalability.
What is Big Data?
Big Data is a term used to describe extremely large and complex datasets that cannot be easily processed or analyzed using traditional data processing tools.
With the boom of digital technologies, we generate vast amounts of data from various sources such as social media, sensors, online transactions, etc. Big Data encompasses all this information, and it continues to grow rapidly.
Importance of a Data Warehouse
For organizations that need to manage and analyze large amounts of data, a data warehouse is essential. It enables them to make informed decisions based on the data, by providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s data in one place.
Importance of a Data Warehouse
Centralized Data Storage: With a data warehouse, all data is stored in one place, making it easier to manage and analyze. This eliminates the need for businesses to search through multiple sources to find the data they need.
Data Integration: A data warehouse allows businesses to integrate data from various sources, including applications, relational databases, and external sources. This makes it possible to combine data from different systems and gain a more complete view of business operations.
Efficient Analysis: With a data warehouse, businesses can perform complex queries, data analysis, and reporting to derive actionable insights. This enables them to make informed decisions based on their data.
Scalability and Performance: A data warehouse can handle large datasets and provide high-performance processing. This makes it possible for businesses to store and analyze vast amounts of data, even as their needs grow over time.
Traditional Data Warehouse Challenges
Traditional data warehousing solutions had many challenges that made them insufficient for managing and analyzing Big Data. Some of these challenges include:
- Lack of Scalability
- Lack of Data Integration:
- High Cost
- Low Performance
- Lack of Real-time Processing and Analysis
Introduction to AWS Redshift
What is AWS Redshift?
AWS Redshift is a cloud-based data warehousing service that allows businesses to store and analyze large amounts of structured and semi-structured data in a scalable and cost-effective manner. It is designed to handle petabyte-scale data processing and analysis tasks and is a fully managed data warehouse service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
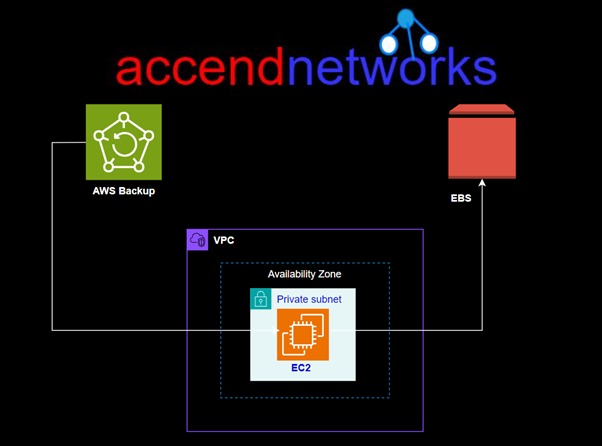
Redshift Architecture and Components
A Redshift cluster consists of one or more nodes. Each cluster has a leader node and one or more compute nodes.
Leader Node: Manages communication with client applications and coordinates query execution.
Compute Nodes: Execute queries and store data. Each compute node has its CPU, memory, and storage.
Nodes and Node Types
Redshift offers different node types based on your performance and storage requirements:
Dense Compute (DC): Optimized for high performance with SSD storage.
Dense Storage (DS): Optimized for large storage capacity with HDDs.
Redshift Spectrum and Data Lake Integration
Redshift Spectrum allows you to query data directly from Amazon S3 without having to load it into Redshift. This feature enables seamless integration with your data lake, allowing you to extend your data warehouse to exabytes of data in S3.
Use Cases for AWS Redshift.
Data Warehousing: Redshift can be used as a centralized repository for all enterprise data, enabling organizations to store and manage large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
Business Intelligence: Redshift can help organizations process and analyze large volumes of data to uncover insights that can inform business decisions.
Machine Learning: Redshift can be used as a data source for machine learning applications, providing access to large volumes of structured and unstructured data that can be used to train machine learning models.
Data Analytics: With Redshift, organizations can analyze large volumes of data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
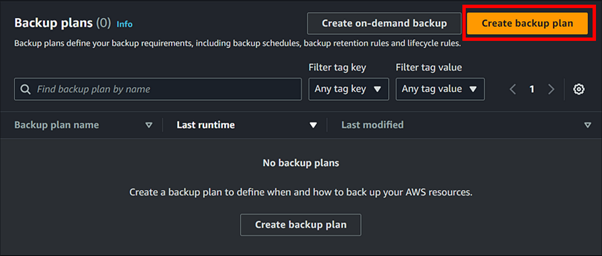
Getting Started with AWS Redshift
Note: In this demo, we will focus on navigating the console and exploring its features rather than creating a Redshift cluster, as provisioning a cluster could incur significant costs.
Access the Redshift Console: Navigate to the AWS Management Console and search for Redshift in the search bar then select Redshift under services.
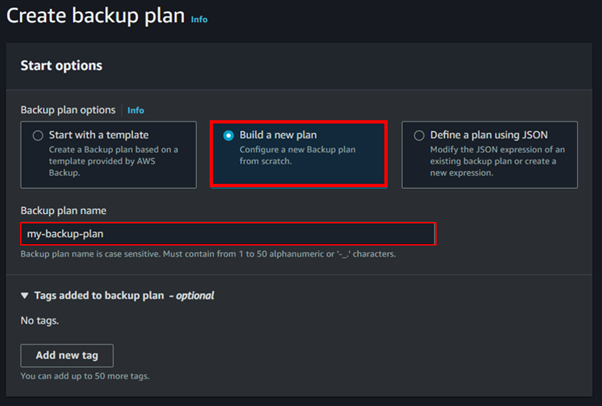
Creating and Configuring a Redshift Cluster
Click on Create cluster.
Choose a cluster identifier, database name, and master user credentials.
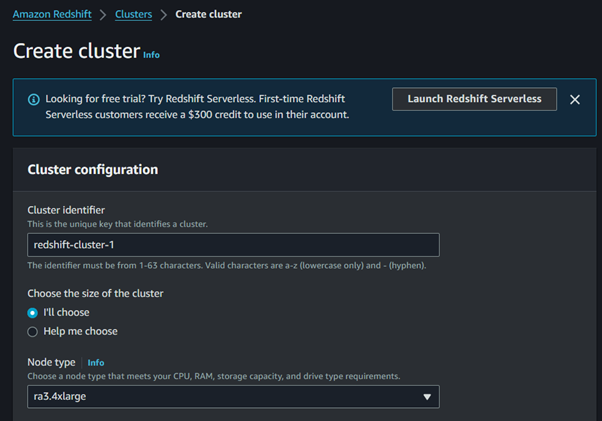
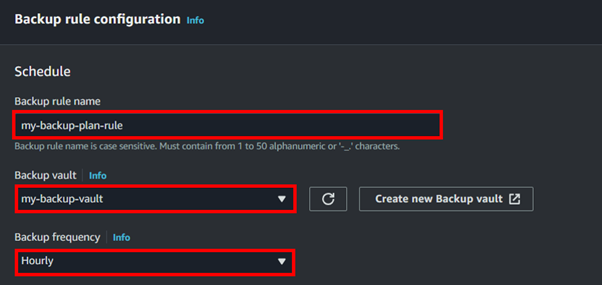
Select the node type and the number of nodes based on your needs.
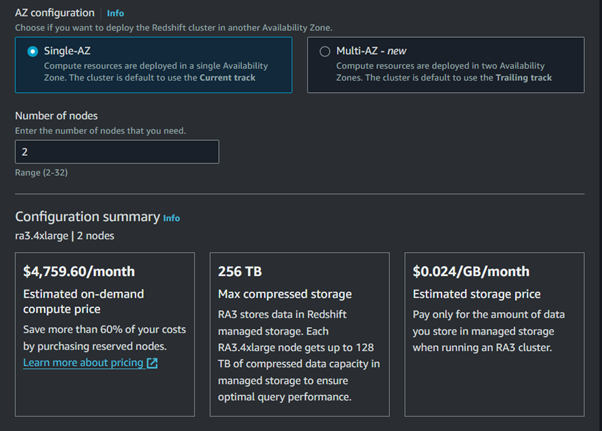
Configure Cluster Settings:
Choose the VPC and subnet group for network settings.
Configure the security settings, including setting up security groups for network access control.
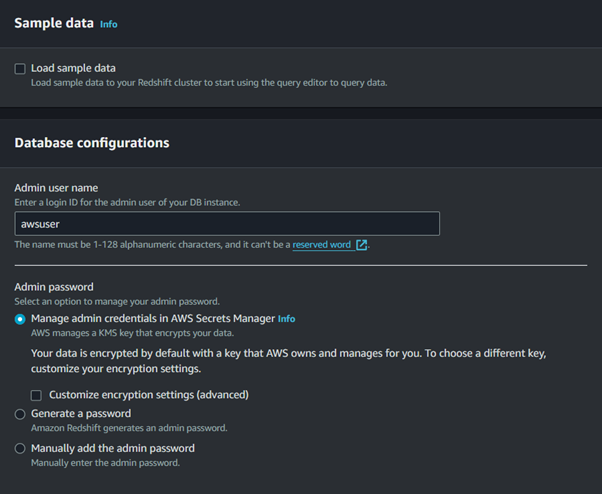
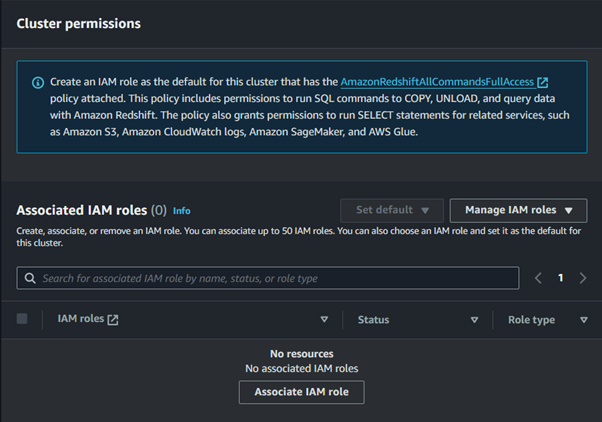
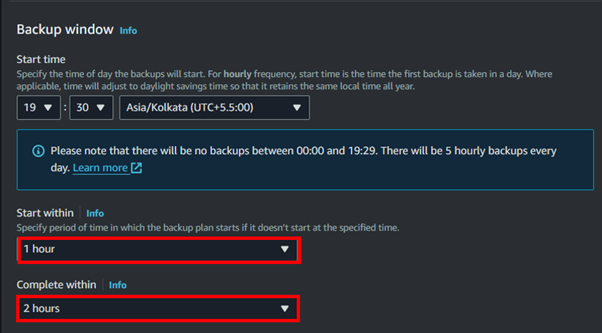
Launch the Cluster:
Review your settings and click on Create cluster.
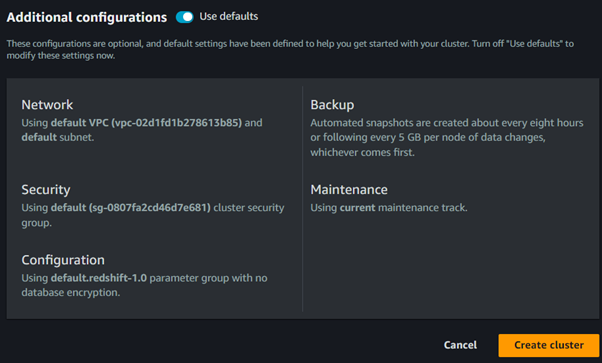
This brings us to the end of this article.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!