AWS Placement Group Hands-On Demo

AWS Placement Groups are a useful tool for improving EC2 instance performance, especially when you need fast communication (low latency) or the ability to handle a lot of data (high throughput). They help you arrange your instances in a way that makes them work better and more reliably. In this demo, we’ll show you how to create and use a Placement Group step-by-step.
What is a Placement Group?
Optimizes low latency and high throughput for EC2 instances by grouping them in the same Availability Zone.
Types of Placement Groups
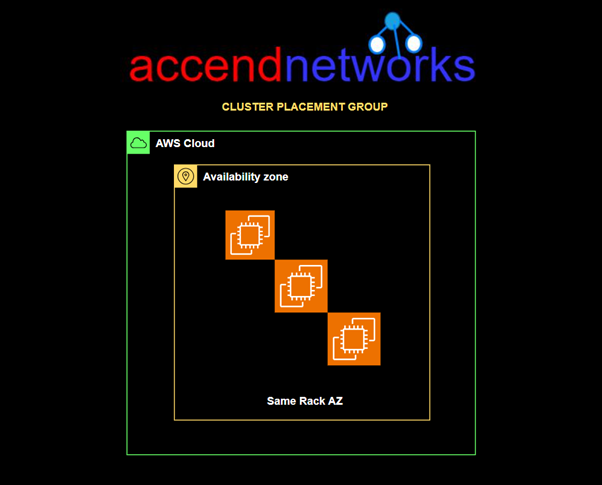
Cluster Placement Group: Packs instances close together inside an Availability Zone. This strategy enables workloads to achieve the low-latency network performance necessary for tightly coupled node-to-node communication that is typical of HPC applications.
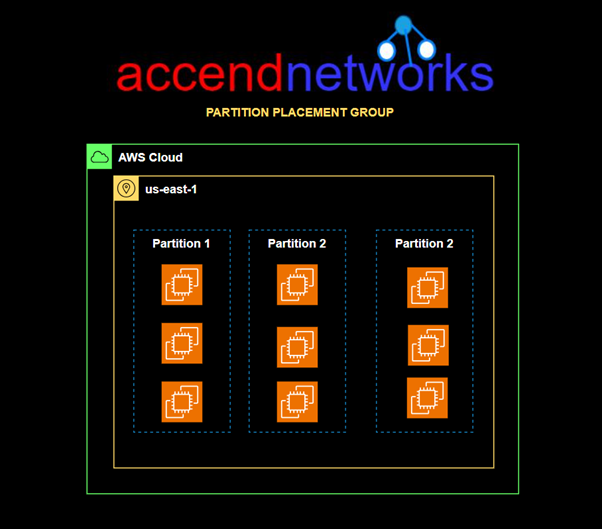
Partition Placement Group: Spread your instances across logical partitions such that groups of the cases in one partition do not share the underlying hardware with groups of instances in different partitions. This strategy is typically used by large distributed and replicated workloads, such as Hadoop, Cassandra, and Kafka.
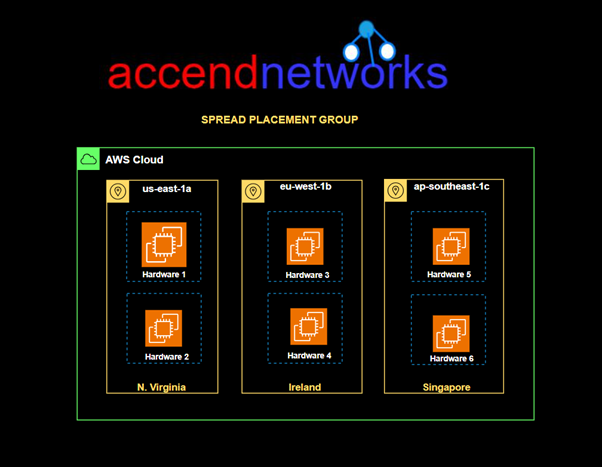
Spread Placement Group: Strictly places a small group of instances across distinct underlying hardware to reduce correlated failures.
A spread placement group is a group of instances that are each placed on distinct racks, with each rack having its own network and power source.
Why use Placement Group?
Placement groups help us to launch a bunch of EC2 instances close to each other.
This can work well for applications exchanging a lot of data and can provide high performance with collocation.
All nodes within the placement group can talk to all other nodes within the placement group at the full line rate of 10 Gbps single traffic flow without any slowing due to over-subscription.
Let’s dive into the hands-on lab.
Step 1: Sign in to AWS Management Console
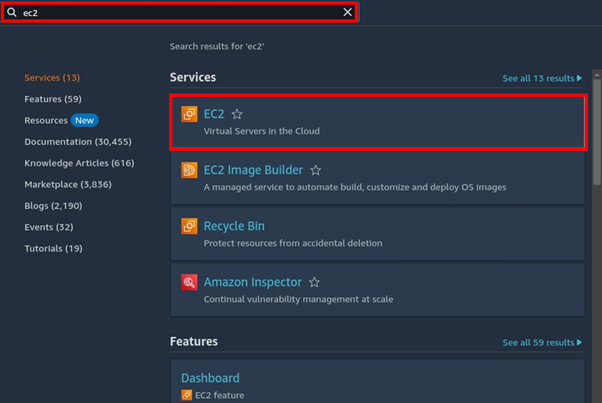
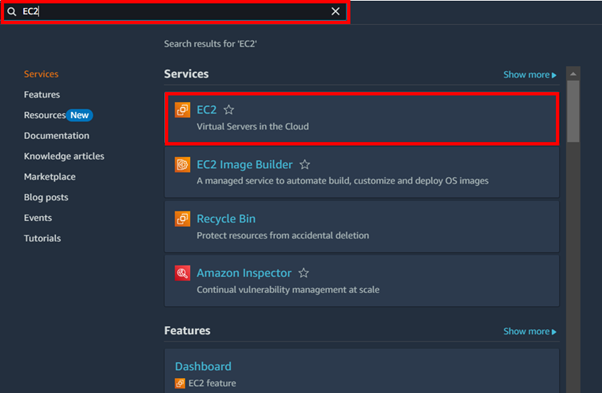
Login to your AWS account from the AWS console, in the search bar, type EC2 then select EC2 Under services.
Step 2: Create EC2 Placement Groups as desired.
Navigate to the left side of EC2 then select placement group.
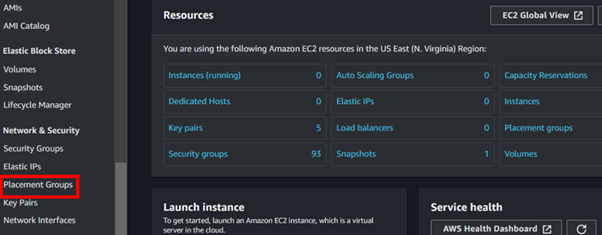
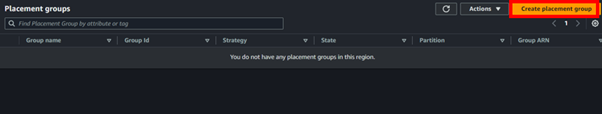
Click Create Placement Group
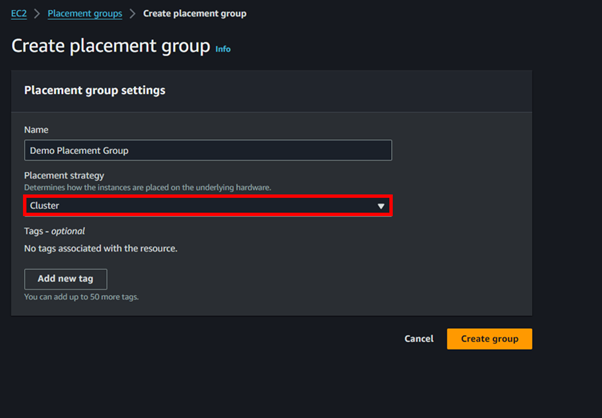
On the Create Placement Group dashboard, enter the name and select a placement strategy to determine how the instances are to be placed on the underlying hardware.
- a) For the Cluster placement group, in the placement strategy dropdown, select the cluster option.
b) For Spread Placement Group, in the placement strategy dropdown, select the option as spread and select Spread Level as either Host or Rack.
c) For Partition Placement Group, in the placement strategy dropdown, select the option as Partition and in the Number of Partitions dropdown select several partitions that you want to create in this placement group.
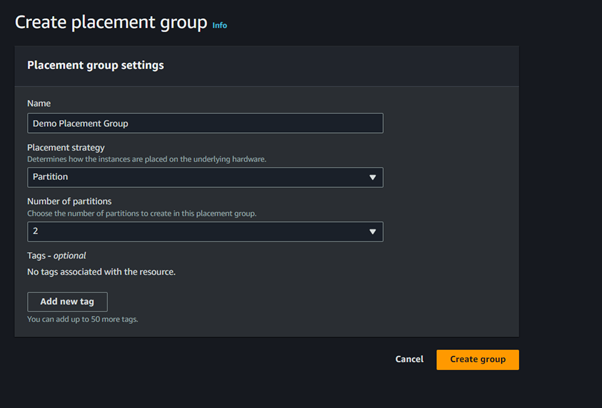
I settled on a Cluster placement Group, and my placement Group has been successfully created.
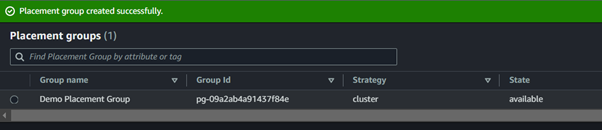
Step 3: Create EC2 instance and assign placement group to it.
We will now go ahead and launch an EC2 Instance and add the Instance to our placement Group.
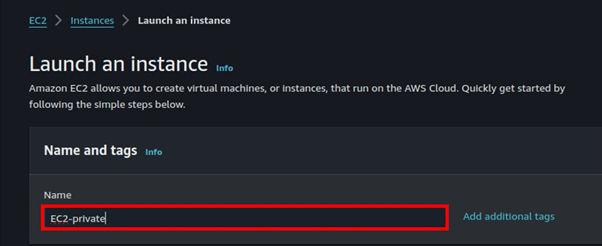
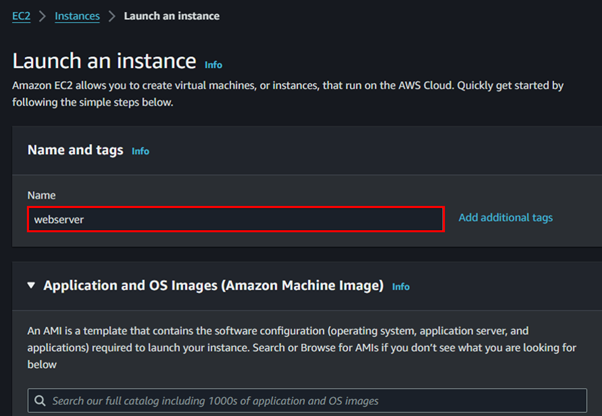
Select instances in the EC2 dashboard then click Launch Instance, In the launch Instance dashboard, provide your Instance details.
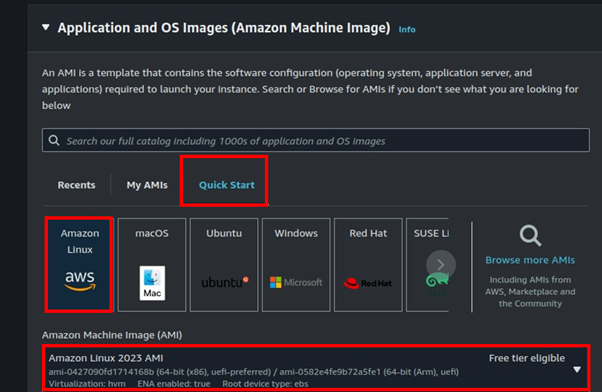
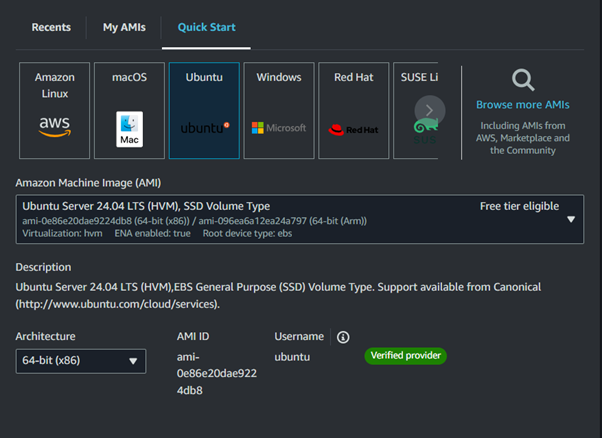
Select your preferred OS and Machine Image.
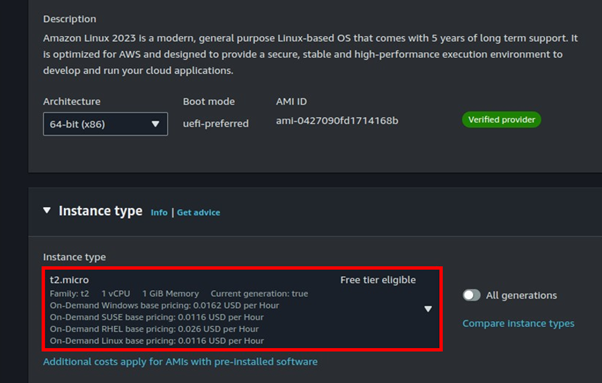
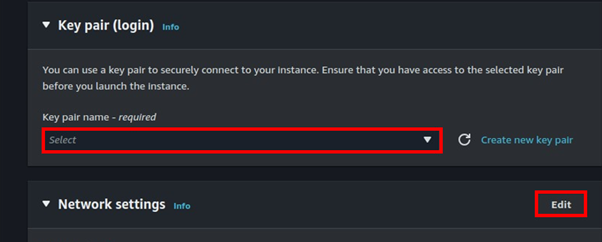
Move with the free tier eligible Instance, then select your key pairs.
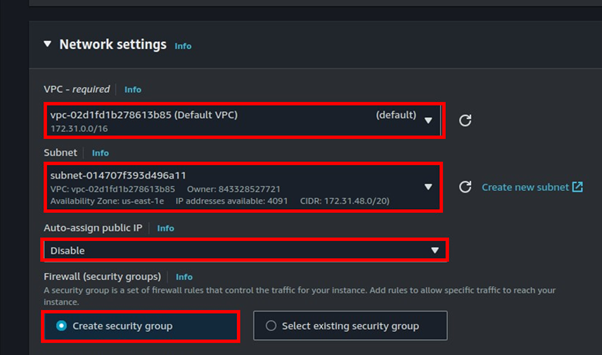
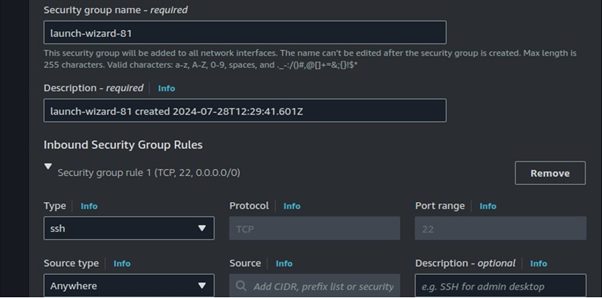
Leave networking as default, and select your security groups.
Leave storage as default, scroll down.
In the advanced section, expand and then scroll all the way down,
In the advanced section, expand and then scroll down,
In the placement group section, select the placement group you have just created.
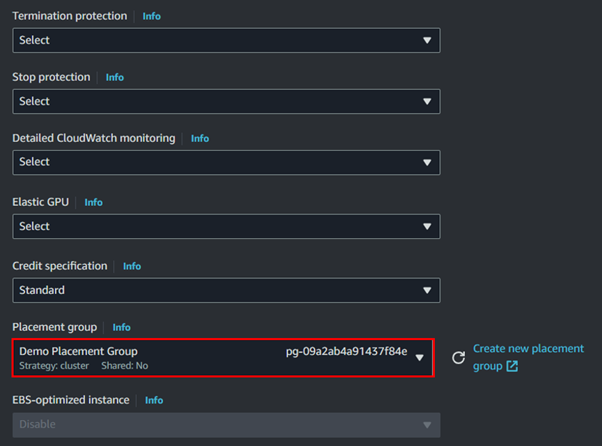
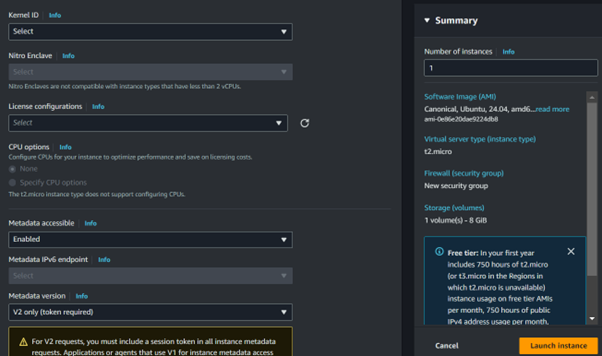
Since t2. Micro is not supported for the Cluster placement group; I will not click Launch.
That’s it, from this demo, I hope you now Know how to create a placement group.
Make sure to delete the placement group, as it is always a good practice to clean up resources.
Since t2. Micro is not supported for the Cluster placement group; I will not click Launch.
That’s it, from this demo, I hope you now Know how to create a placement group.
Make sure to delete the placement group, as it is always a good practice to clean up resources.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!