A Comprehensive Overview Amazon Elastic File System: Shared File Storage for Your AWS Workloads
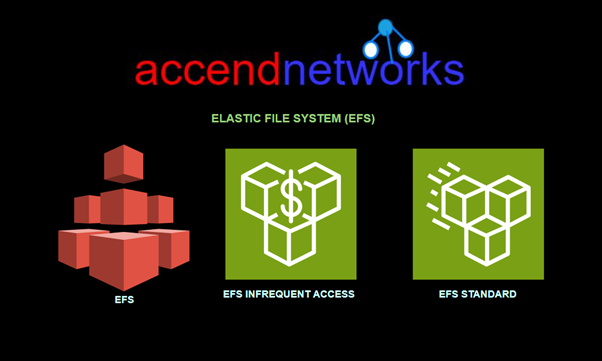
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a fully managed service that enables easy file storage management for applications and workloads on AWS. In the blog, we will provide an overview of EFS architecture, key features, and how it compares to other storage options.
There are multiple storage offerings in AWS, each designed to meet different storage needs. Some of the most popular storage solutions include:
- AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store)
- AWS EFS (Elastic File System)
What is Amazon EFS
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is a scalable, fully managed, cloud-based file storage service provided by Amazon Web Services. It is designed to work with Linux-based workloads and can be mounted on Amazon EC2 instances, containers (ECS), and AWS Lambda functions across multiple Availability Zones within an AWS region.
AWS EFS Architecture
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is AWS’s implementation of NFS (Network File System) v4. With Amazon EFS, you can grow and shrink storage automatically as you add or remove files, providing read-after-write consistency for your data.
Amazon EFS file systems can be accessed by multiple compute instances like EC2, ECS, or Lambda within a VPC in various Availability Zones (AZs) within an AWS region. Additionally, Amazon EFS can connect to multiple VPCs via VPC Peering connections and can even be accessed from on-premises environments through VPN or Direct Connect.
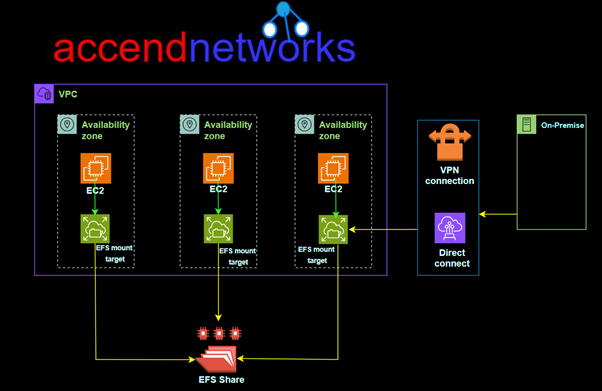
Mount Targets
A mount target in Amazon EFS is an endpoint that allows EC2 instances to connect to and access an EFS file system. Each mount target is associated with a specific Availability Zone (AZ) and provides network access to the EFS file system within that zone.
Key Features of Mount Targets in EFS:
Per AZ Mount Target: To access an EFS file system from EC2 instances in a specific AZ, you must create a mount target in that AZ, enabling VPC-based connectivity.
Security Group Control: Each mount target can have its security group attached to control traffic. Typically, you must allow inbound traffic on NFS port 2049 from EC2 instances accessing the EFS.
Highly Available: By creating a mount target in each AZ, EFS ensures high availability and fault tolerance.
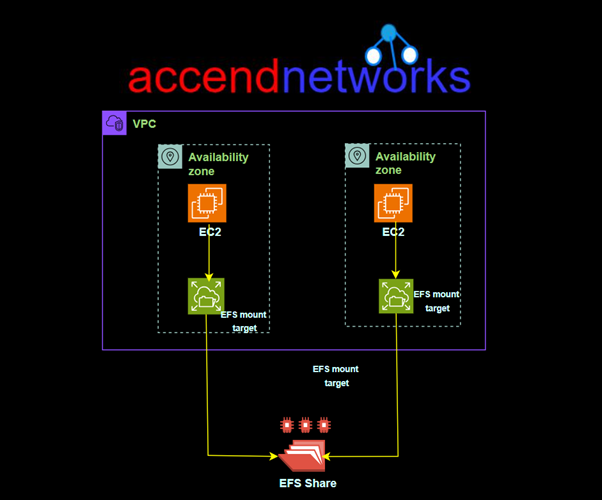
For standard Amazon EFS file systems, you need to create a mount target in each AZ within your AWS region.
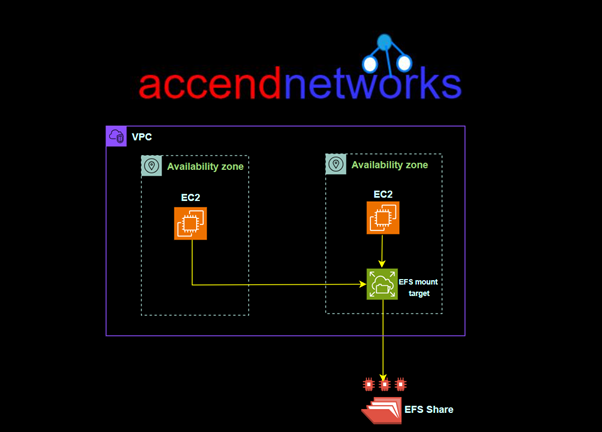
When using the One Zone storage class, however, only a single mount target can be created in the AZ where the file system is located.
Throughput Modes
Amazon offers two throughput modes:
Bursting mode: This is the default and allows throughput to scale based on the amount of data stored.
Provisioned mode: Suitable for applications that require higher throughput than what is provided by bursting mode.
Performance Modes
There are two performance modes available for Amazon EFS:
General Purpose (recommended): Best for most workloads and is ideal for latency-sensitive applications.
Max I/O: Designed for use cases where many EC2 instances are accessing the file system simultaneously, such as big data and media processing applications.
Amazon EBS vs EFS: A Key Comparison
Both Amazon EBS and Amazon EFS offer storage solutions, but they are designed for different purposes. Amazon EBS is a block storage solution used for a single EC2 instance and is ideal for high-performance storage, whereas Amazon EFS is designed for shared file storage across multiple EC2 instances, providing elastic scalability without manual intervention.
If you’re choosing between Amazon EBS vs EFS, EFS is the better option for shared storage and file-based workloads, while EBS is optimal for individual instances with higher performance needs.
When to Use Amazon EFS
Amazon Elastic File System is an ideal solution for workloads that require scalable, shared file storage. Whether you’re running an application in AWS Lambda, working on big data analysis, or simply need shared storage for multiple EC2 instances, Amazon EFS provides a reliable, fully managed, and elastic solution.
Conclusion
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is robust and scalable. With its elastic capabilities, seamless AWS integration, and strong security features, Amazon EFS is ideal for a wide range of cloud storage needs.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!

[…] SFTP, FTPS, and FTP. The service is highly scalable, allowing users to integrate with Amazon S3 or Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) for backend storage. With AWS Transfer Family, businesses can replace their traditional file […]