Amazon ECR: Managing Docker Images with Elastic Container Registry
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a fully managed container image registry service designed to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images securely. ECR integrates seamlessly with Amazon ECS, EKS, and other AWS services, enabling efficient containerized application deployment and simplifying DevOps workflows. This blog provides an overview of Amazon ECR and how to set it up though the AWS console.
What is Amazon ECR
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) is a secure, scalable, and reliable AWS-managed container image registry service that supports private repositories with resource-based permissions using AWS IAM.
Private and Public Repositories
ECR supports two repository types, making it flexible for both internal usage and public sharing.
- Private Repositories: Suitable for storing proprietary images that are accessible only within your organization. Access is controlled through AWS IAM, ensuring your container images remain secure.
- Public Repositories: ECR’s Public Gallery allows you to host images publicly, making them available for community use. This is useful for open-source projects or sharing container images with a broad audience.
Using private and public repositories enables a hybrid approach to managing your image distribution, where sensitive applications can remain secure within private repositories while open-source or shareable images can be accessed publicly.
Why Use Amazon ECR?
Amazon ECR offers robust capabilities and benefits that make it a preferred choice for Docker image management:
- Security and Compliance: With encryption in transit, image scanning, and integrated AWS IAM policies, Amazon ECR ensures high security for your Docker images.
- Scalability: ECR scales automatically, handling large volumes of Docker images without requiring manual configuration or intervention.
- Integration with AWS Services: ECR seamlessly integrates with Amazon ECS, EKS, CodePipeline, and CodeBuild, enabling automated deployments and CI/CD workflows.
- Simplified Workflow: ECR eliminates the need to set up and manage your container image registry, reducing operational overhead.
Getting Started with Amazon ECR
Step 1: Setting Up an Amazon ECR Repository
To begin using Amazon ECR, you need to create a repository where your Docker images will be stored.
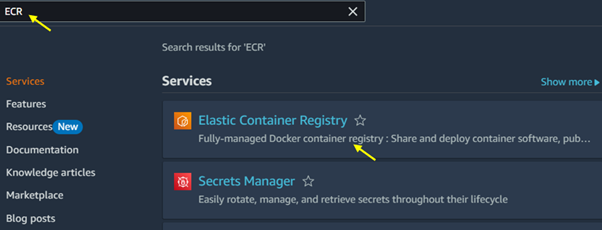
Open the Amazon ECR Console: Go to the Amazon ECR Console. Then type ECR in the search bar and select ECR under services.
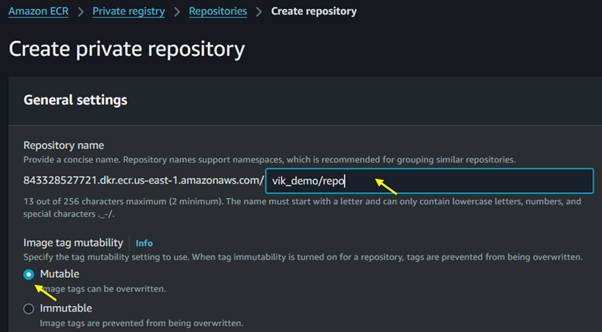
Click on Create Repository.
Configure Settings: Provide a name for your repository and configure settings like image scanning and encryption.
Repository Policies: Set access permissions for your repository. By default, repositories are private, but you can adjust policies for specific users, roles, or accounts.
For Image tag mutability, select immutable. When tag mutability is turned on, tags are prevented from being overwritten.
Step 2: Authenticating Docker to ECR
After creating a repository, you must authenticate Docker to interact with Amazon ECR. AWS provides a simple command to obtain and configure Docker login credentials.
Run Authentication Command:
Copy code
aws ecr get-login-password –region <region> | docker login –username AWS –password-stdin <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
Replace <region> and <aws_account_id> with your AWS region and account ID.
Verify Authentication: You should see a “Login Succeeded” message, confirming Docker’s successful authentication with Amazon ECR.
Security and Access Management
ECR is highly secure, leveraging AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access. Users and roles can be granted specific permissions, ensuring secure access to repositories and images.
- IAM Policies: Using IAM policies, you can control who has access to view, upload, or delete images.
This control allows fine-grained security, ensuring your images are accessible only to those with explicit permission.
Automating Docker Deployments with Amazon ECR
Integrating Amazon ECR with other AWS services lets you automate container image deployments, providing agility in CI/CD pipelines. Here’s a high-level overview of how ECR can streamline the deployment process.
CI/CD Integration with CodePipeline and CodeBuild: Amazon ECR integrates with CodePipeline and CodeBuild to automate Docker image builds, tests, and deployments.
ECS and EKS Deployments: ECR is the primary image registry for Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS, allowing you to quickly deploy containerized applications.
Scheduled Image Scanning: Regularly scan your images for vulnerabilities with Amazon ECR’s built-in scanning feature, which provides insight into image security.
Best Practices for Managing Docker Images in Amazon ECR
Enable Image Scanning: Regular scanning helps identify vulnerabilities in your Docker images, adding an extra layer of security.
Use Lifecycle Policies: Lifecycle policies allow you to define rules for image retention, which helps optimize storage costs by automatically deleting older, unused images.
Implement Access Control: Use IAM policies to manage permissions, ensuring only authorized users can push or pull images from the repository.
Use Version Tagging: Consistent version tagging helps in identifying and managing different versions of an image efficiently, especially in multi-environment deployments.
Conclusion
Amazon ECR offers a scalable, secure, and fully managed solution for managing Docker images. It streamlines the containerization process, allowing teams to focus on building and deploying applications without worrying about registry management.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!