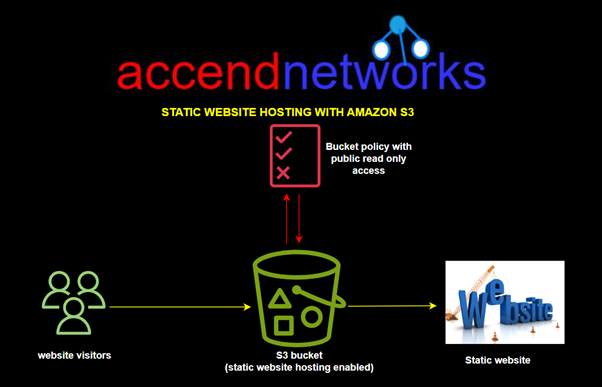
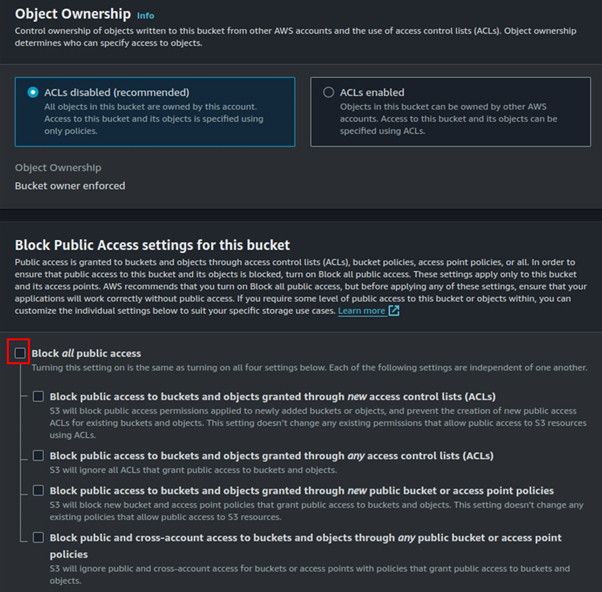
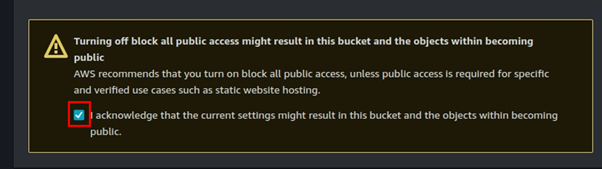
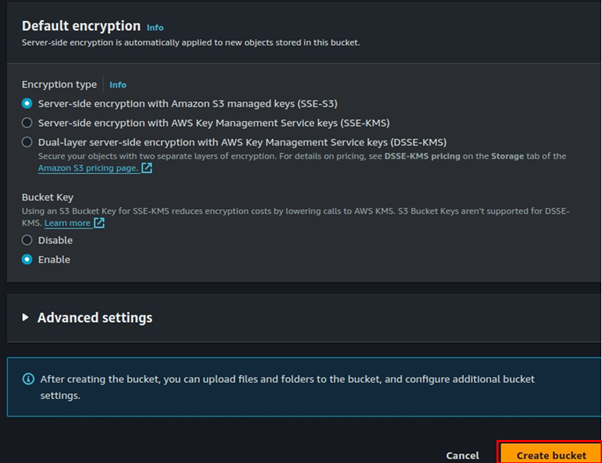
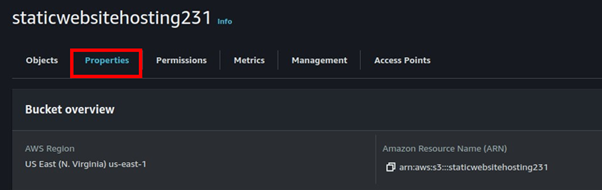
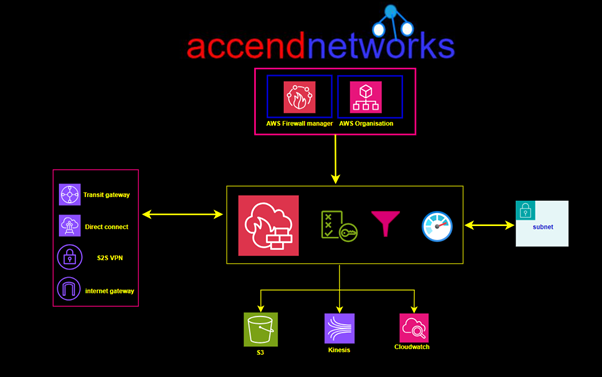
How to Connect to Meeting Audio and Do Content Sharing
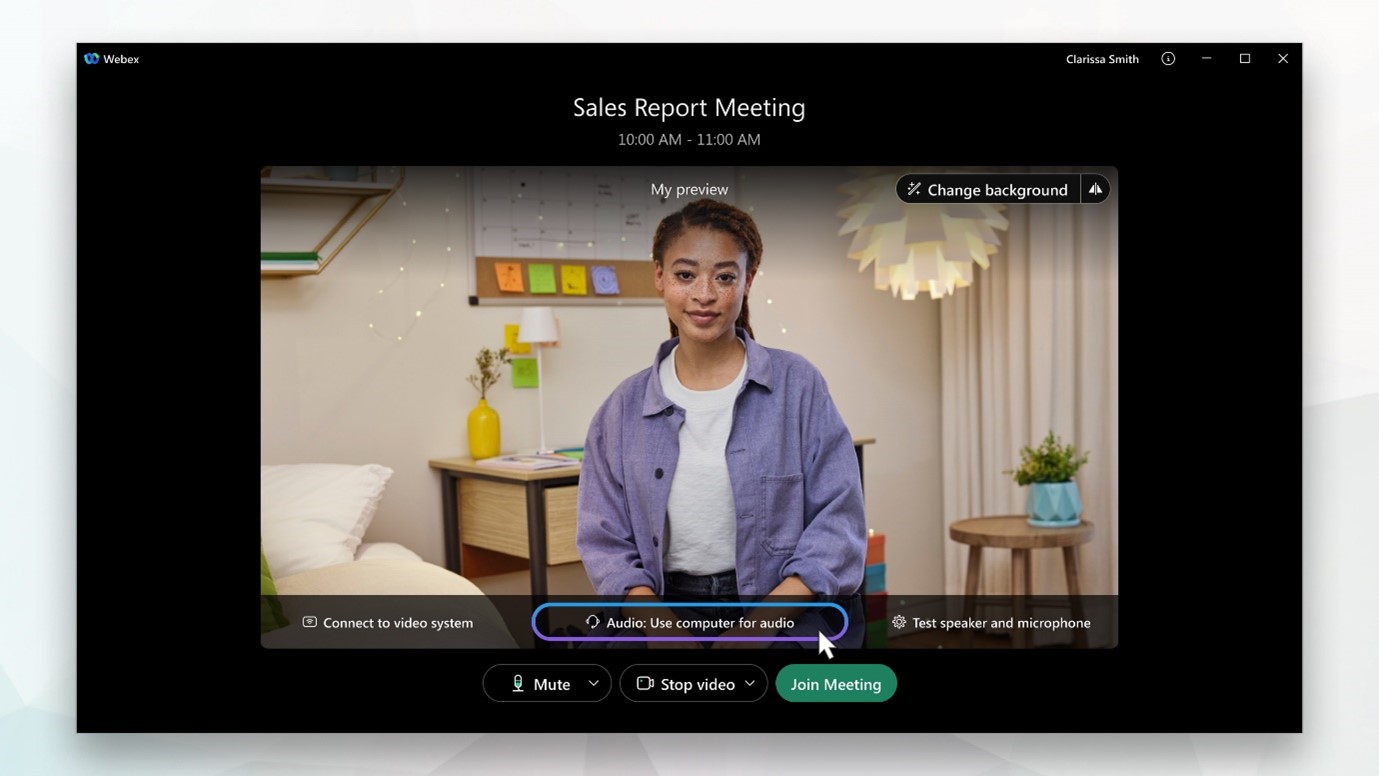
Cisco WebEx offers several audio connection types for meetings, including using your computer, phone, or internet. Below are the types of the various options available to connect to WebEx meeting audio.
- Computer audio (Use internet for audio):
Use speakers or headphones to connect to audio over the internet. This option is considered to have the highest audio quality. If your computer has a supported sound card and an internet connection, you can also use a headset to join the meeting. - Call me:
Enter a phone number for the meeting to call, such as your home or work number. This option allows you to move around while still participating in the meeting. - Call in:
Dial into the meeting from your phone when it starts. You can find a list of global call-in numbers after joining the meeting. You can also use this option if your battery is low, and you want to switch to audio-only mode to save battery life. - Don’t connect to audio:
This option prevents you from hearing audio in the meeting, but you can still use your device to share content.
Content sharing in WebEx meeting:
When you share content in Webex App, everyone in the meeting can easily see what’s being discussed. Anyone can share content, but only one person can share at a time.
If you are a host or cohost of the meeting, you can disable sharing for all other participants during a meeting.
You can share content when you’re connected to a room or desk device.
Step1: During a meeting, select ![]()
Step2: When you’re sharing content with video or audio, you should check these options:
Optimization drop-down list:
- Automatically Optimize—Chooses the best optimization for your content type.
- Optimize for text and images—Displays text and images in your shared content at the highest resolution and clarity possible.
- Optimize for motion and video—The video plays back much more smoothly, as some resolution is sacrificed in Favor of a higher frame rate to reduce lag and increase fluidity in your shared video, animation, or dynamic content.
- Share computer audio—Allows others to hear your computer audio in addition to your microphone audio.
Step3: Choose the screen or application that you want to share.
- If you share your screen, it shows your Webex App windows, by default. To prevent them from being visible to other participants, hide Webex App.
- For applications share all or an individual application window. To share your Webex App meeting window and all floating windows, you must select Share all windows from an application.
- Hold Shift to select multiple applications. Everyone in the meeting sees one of the shared applications at a time only.
- If you don’t see the app that you want to share, scroll to see all your open apps, or drag the resize handle
 on any of the four corners or sides to make the window larger or smaller.
on any of the four corners or sides to make the window larger or smaller.
Step4: Check the Show me in front of presentation check box to show your video in front of the shared content.
NOTE: This option isn’t available when you share your Webex App meeting window and all floating windows.
Step5: While you’re sharing, you can select the following:
 indicator shows your network connection and CPU usage, the
indicator shows your network connection and CPU usage, the  indicator appears when the meeting is being recorded, and the indicator appears when the meeting is locked.
Step6: When you want to stop
indicator appears when the meeting is being recorded, and the indicator appears when the meeting is locked.
Step6: When you want to stop  sharing, click Stop at the top of the screen.
sharing, click Stop at the top of the screen.
- Pause
 to pause sharing your screen or application.
to pause sharing your screen or application. - Resume
 to resume sharing your screen or application.
to resume sharing your screen or application.
 indicator shows your network connection and CPU usage, the
indicator shows your network connection and CPU usage, the  indicator appears when the meeting is being recorded, and the indicator appears when the meeting is locked.
Step6: When you want to stop
indicator appears when the meeting is being recorded, and the indicator appears when the meeting is locked.
Step6: When you want to stop  sharing, click Stop at the top of the screen.
sharing, click Stop at the top of the screen.