Understanding AMI in AWS: A definitive guide to cloud resilience
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) and Snapshots play crucial roles in the storage, replication, and deployment of EC2 instances. This guide not only demystifies the significance of AMIs but also unveils effective AWS backup strategies, including the vital process of taking AMI backups.
What is an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)?
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is an image that provides the software that is required to set up and boot an Amazon EC2 instance. Each AMI also contains a block device mapping that specifies the block devices to attach to the instances that you launch.
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is a template that contains the information required to launch an EC2 instance, it is the encapsulation of server configuration. Each AMI also contains a block device mapping that specifies the block devices to attach to the instances that you launch.
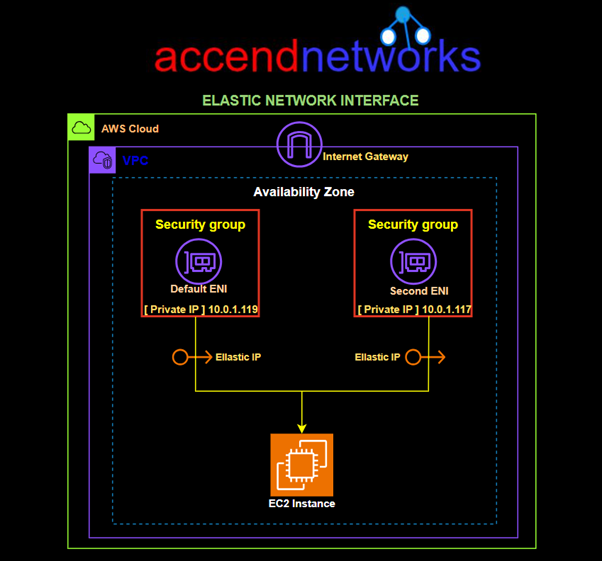
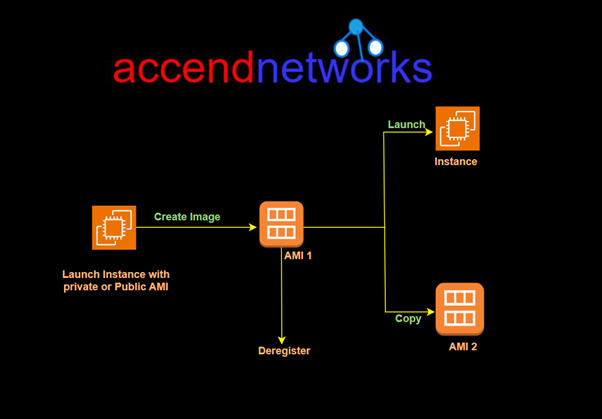
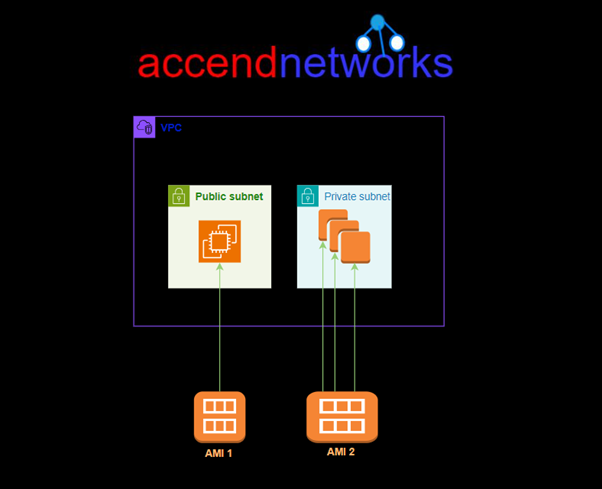
You can launch multiple instances from a single AMI when you require multiple instances with the same configuration. You can use different AMIs to launch instances when you require instances with different configurations, as shown in the following diagram.
You can launch multiple instances from a single AMI when you require multiple instances with the same configuration. You can use different AMIs to launch instances when you require instances with different configurations, as shown in the following diagram.
Key Components of an AMI:
Root Volume: Contains the operating system and software configurations that make up the instance.
Launch Permissions: Determine who can use the AMI to launch instances.
Block Device Mapping: Specifies the storage devices attached to the instance when it’s launched.
AMIs can be public or private:
Public AMIs: Provided by AWS or third-party vendors, offering pre-configured OS setups and applications.
Private AMIs: Custom-built by users to suit specific use cases, ensuring that their application and infrastructure requirements are pre-installed on the EC2 instance.
Types of AMIs:
EBS-backed AMI: Uses an Elastic Block Store (EBS) volume as the root device, allowing data to persist even after the instance is terminated.
Instance store-backed AMI: Uses ephemeral storage, meaning data will be lost once the instance is stopped or terminated.
Why Use an AMI?
Faster Instance Launch: AMIs allow you to quickly launch EC2 instances with the exact configuration you need.
Scalability: AMIs enable consistent replication of instances across multiple environments (e.g., dev, test, production).
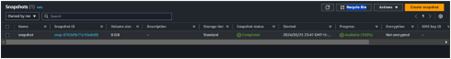
Backup and Recovery: Custom AMIs can serve as a backup of system configurations, allowing for easy recovery in case of failure.
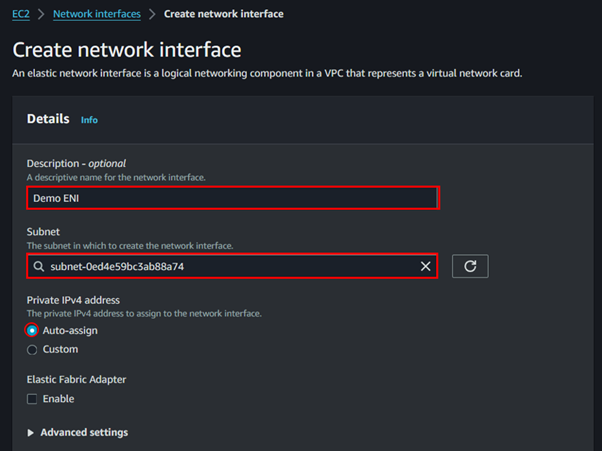
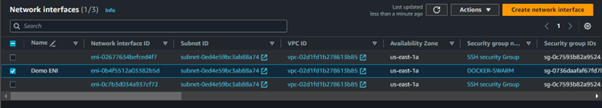
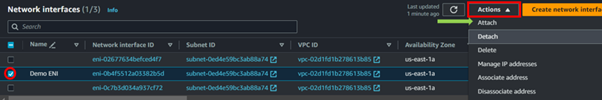
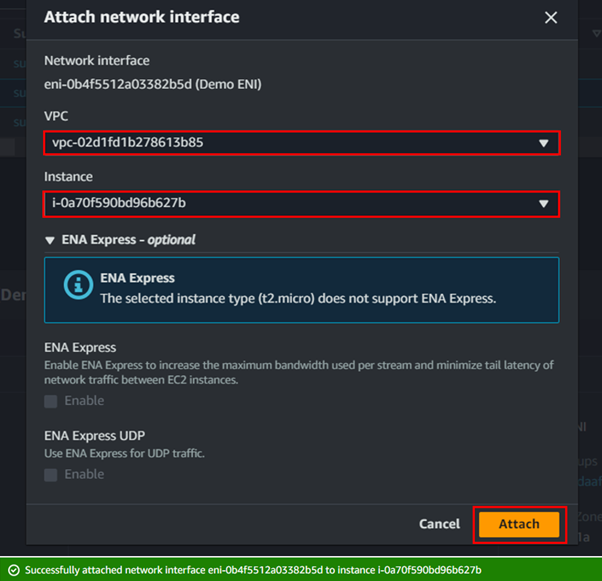
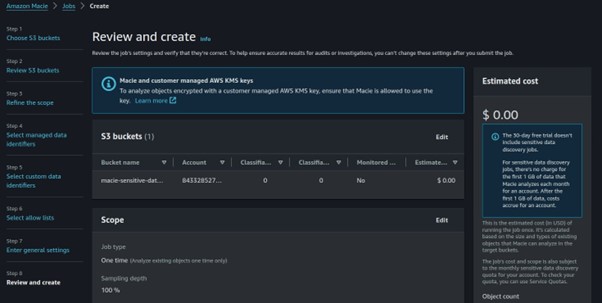
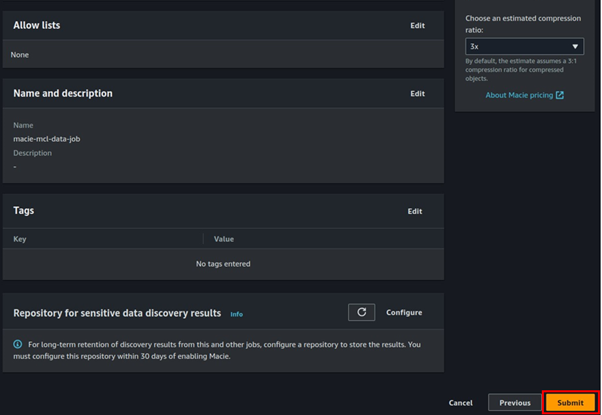
Creating an AMI
Let’s now move on to the hands-on section, where we’ll configure an existing EC2 instance, install a web server, and set up our HTML files. After that, we’ll create an image from the configured EC2 instance, terminate the current configuration server, and launch a production instance using the image we created. Here’s how we’ll proceed:
Step 1: Configuring the instance as desired
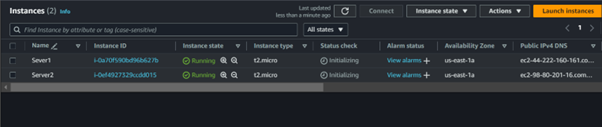
Log in to the AWS Management Console with a user account that has admin privileges, and launch an EC2 instance.
I’ve already launched an Ubuntu machine, so next, I’ll configure Apache webserver and host my web files on the instance.
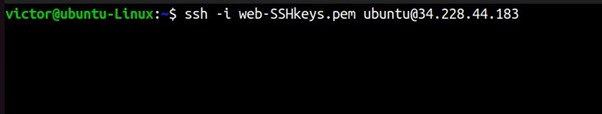
SSH into your machine using the SSH command shown below.
Update your server repository.
Install and enable Apache.
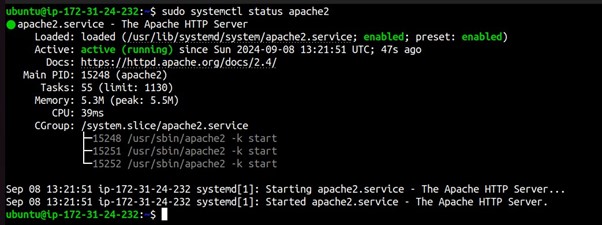
Check the status of the Apache web server.
Now navigate to the HTML directory using the below command.
Use the vi editor to edit and add your web files to the HTML directory, run sudo vi index.html

Exit and save the vi editor.
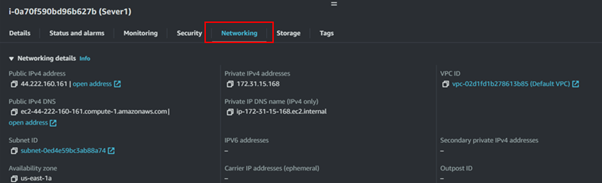
We’ve successfully configured our EC2 instance to host the web application. Now, let’s test it by copying the instance’s IP address and pasting it into your web browser.

Our instance is up and running, successfully hosting and serving and serving our web application.
Step 2: Creating an image of the instance
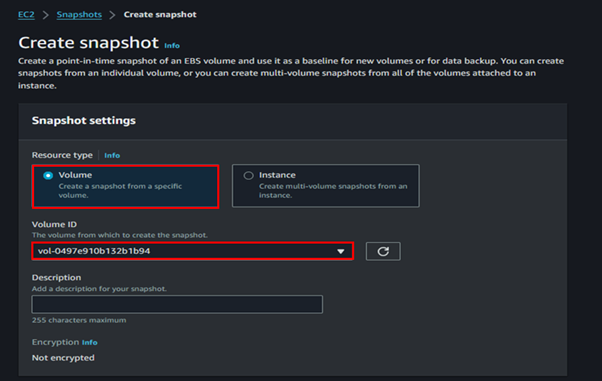
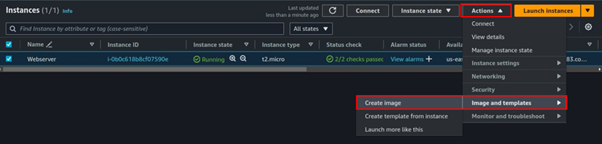
Select the running EC2 Instance, select the actions drop-down button, and navigate to Image and Templates then click Create Image.
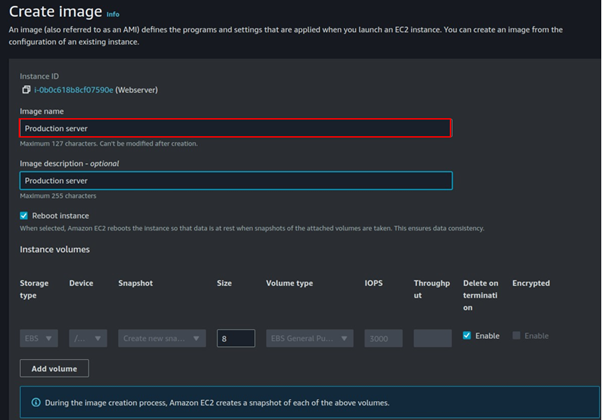
Provide details for your Image
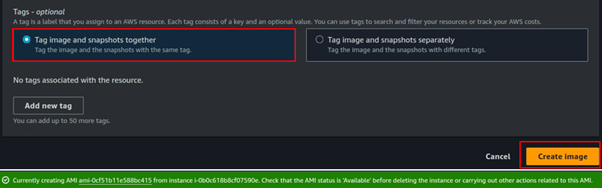
Select tag Image and snapshots together then scroll down and click Create Image.
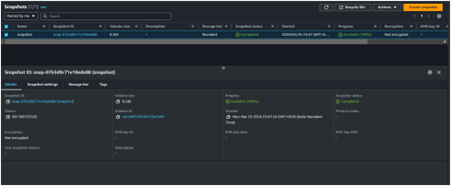
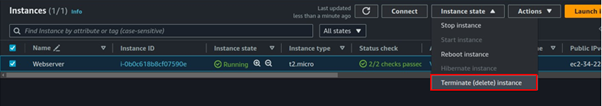
Once the Image is available and ready for use, you can now proceed and delete your setup server.
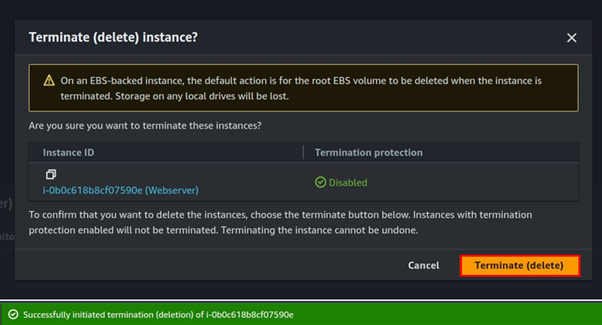
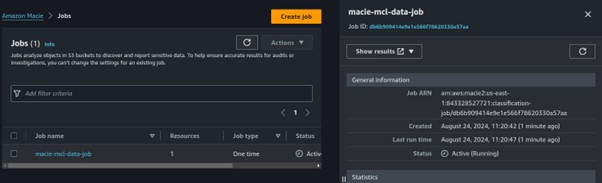
Step 3: Launch new EC2 instance from the created Image.
We will now use the created Image to launch a new EC2 instance, we will not do any configuration since the application has our app already configured.
Let’s proceed and launch our EC2 instance, click launch Instance from the EC2 dashboard.
Under Applications and OS, select my AMI, then select owned by me.
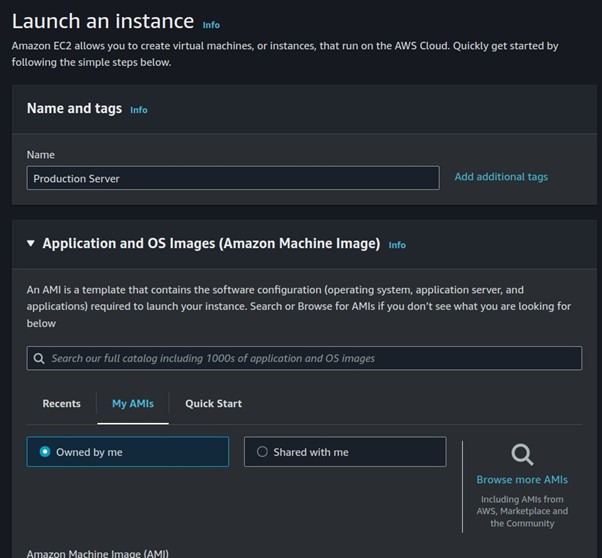
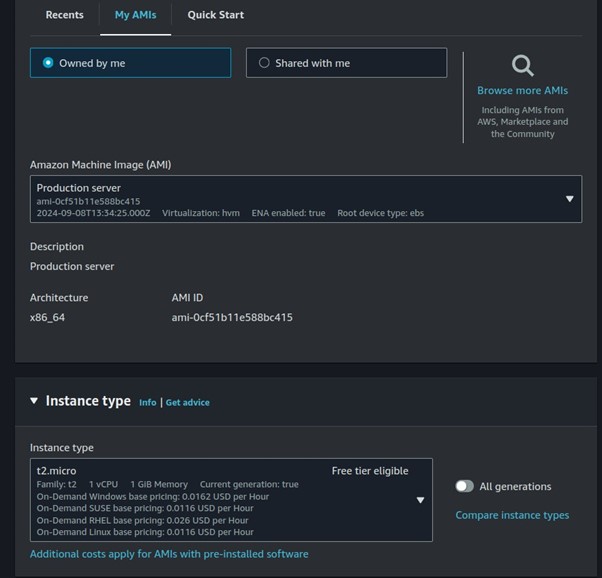
Select t2. Micro, then scroll down.
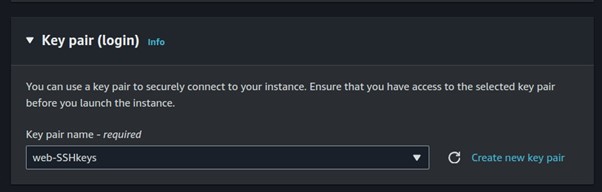
Select your key pairs.
Configure your security groups
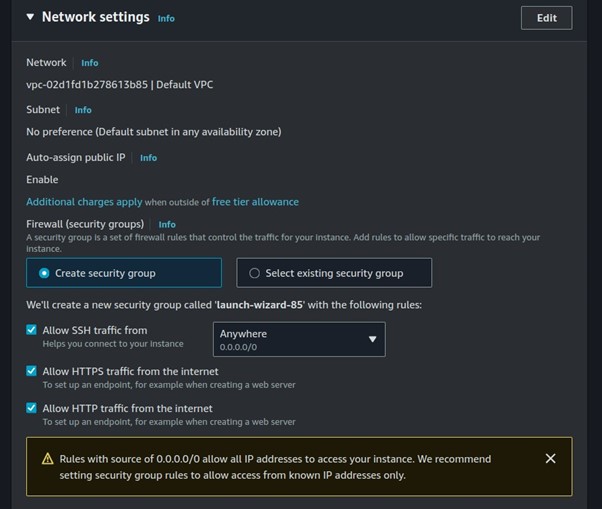
Review and click Create Instance.
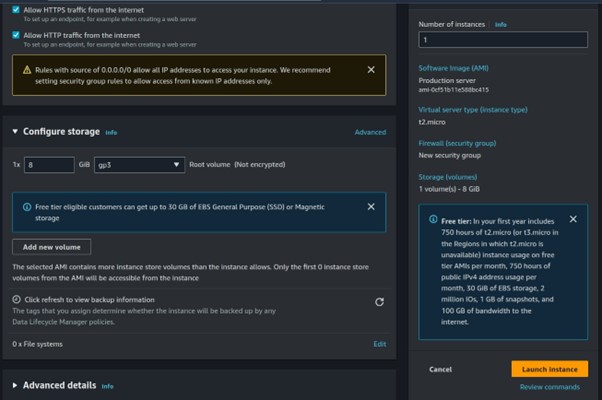
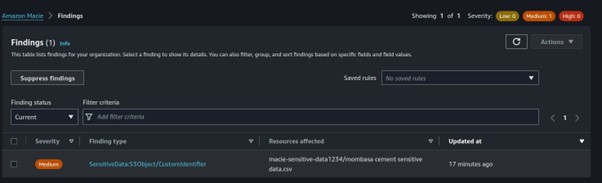
Step 4: Test our application.
Once our application is up and running, grab the public IP and paste it into your browser.
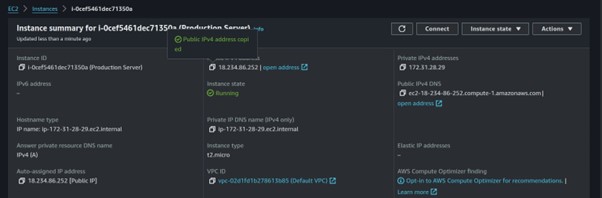
We have created an EC2 instance from an AMI with an already configured application. Application achieved.

Clean up. This brings us to the end of this article.
Conclusion
Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) are fundamental tools in managing EC2 instances. Understanding how to effectively use AMIs can help optimize your AWS environment, improving disaster recovery, scaling capabilities, and data security.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
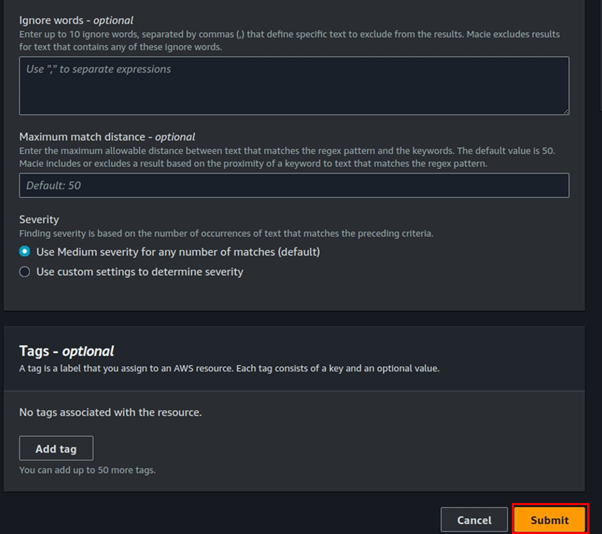
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!