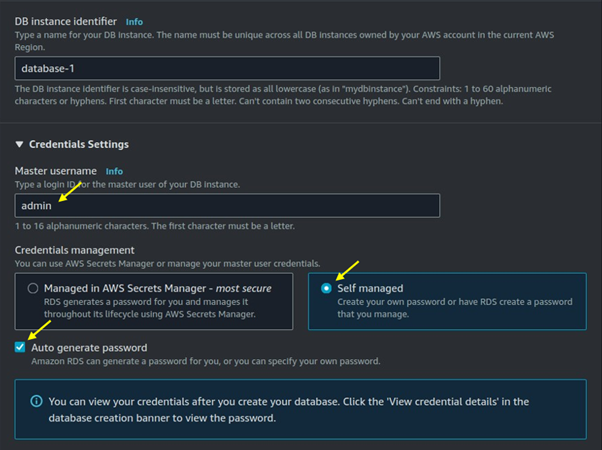
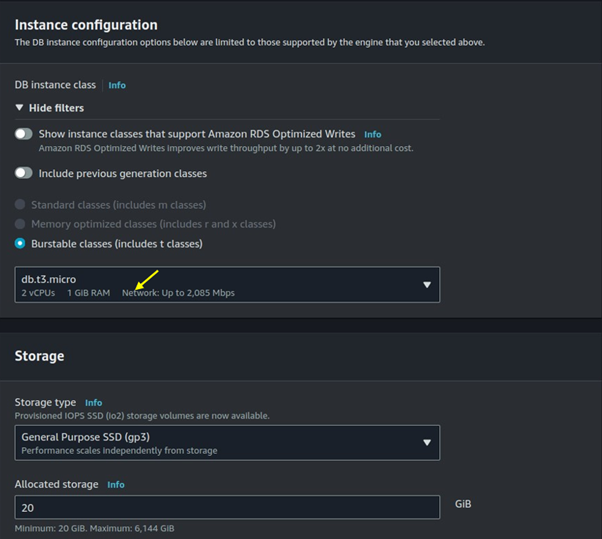
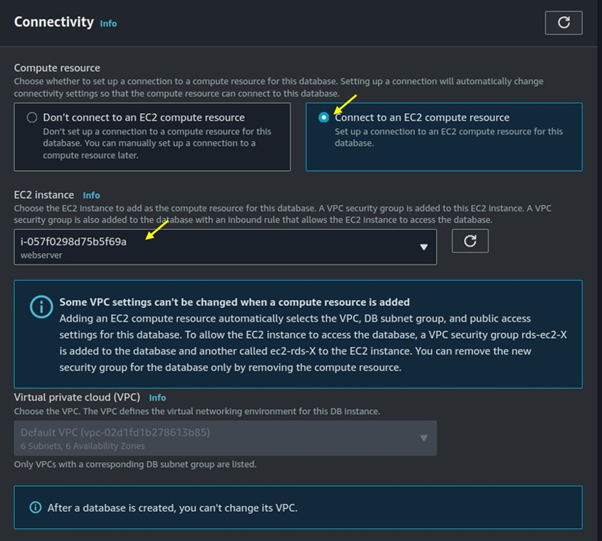
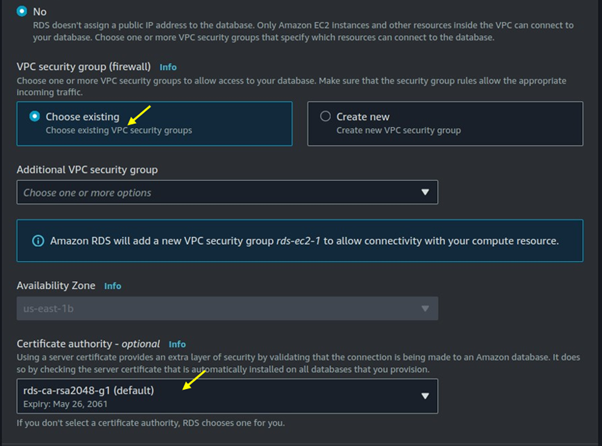
Effortless Job Processing with AWS Batch: A Complete Guide to Scaling Compute Workloads

Efficient job processing is essential for organizations handling complex computing workloads. AWS Batch, Amazon Web Services’ fully managed batch processing service, streamlines this process by automating the scheduling, provisioning, and scaling of compute resources.
What is AWS Batch?
AWS Batch is a fully managed service that enables you to run large-scale compute workloads in the cloud without provisioning resources or managing schedulers. The service takes care of infrastructure management, so you can focus on designing your workflows instead of worrying about underlying resources.
AWS Batch dynamically provisions the optimal quantity and type of compute resources (for example, CPU or memory-optimized instances) based on the volume and specified resource requirements of the batch jobs submitted.
It plans, schedules, and executes your batch computing workloads across the full range of AWS compute services and features, such as Amazon EC2 and Spot Instances.
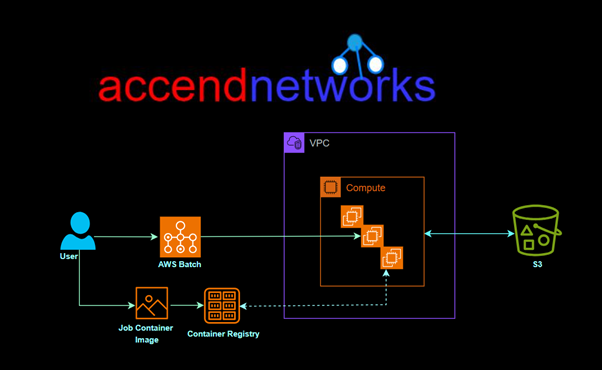
Here’s a breakdown of key components and how AWS Batch works:
Components:
Compute Environments: AWS Batch uses compute environments to manage the infrastructure on which your batch jobs run.
It supports both EC2 instances and AWS Fargate containers as computing resources.
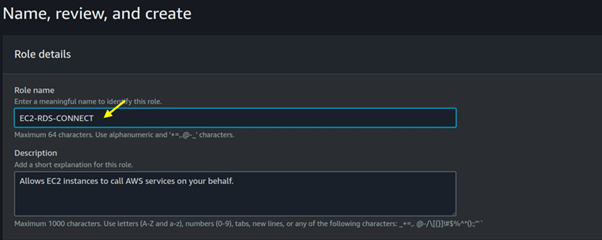
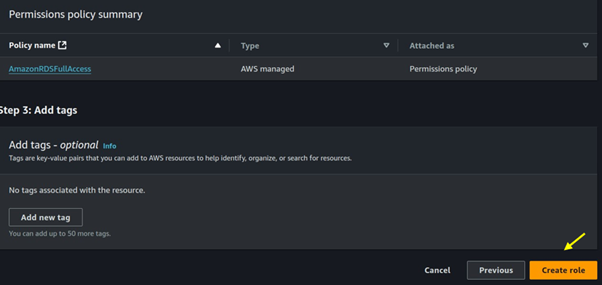
Job Definitions: A job definition specifies how a job is to be run, including the Docker image to be used, the command to be executed, and various parameters.
It encapsulates the information needed for jobs to be submitted to the batch environment.
Job Queues: Job queues are used to submit jobs. You submit a job to a specific queue, and AWS Batch places the job in the queue.
Each queue is associated with one or more priority levels, which determines the order in which jobs are scheduled.
Jobs: Jobs are the unit of work in AWS Batch. Each job is defined by a job definition, and it runs on an Amazon EC2 instance or an AWS Fargate container.
Workflow
Submit Job: Users submit jobs to a specific job queue. The job queue contains a list of jobs that are waiting to run.
Job Scheduler: AWS Batch job scheduler takes care of prioritizing, scheduling, and launching jobs based on the job queue’s priority levels.
Compute Environment Allocation: The job scheduler allocates compute resources from the defined compute environment to run the jobs.
Run Jobs: Jobs are executed on EC2 instances or Fargate containers based on the specifications in the job definition.
Monitoring and Logging: AWS Batch provides monitoring through Amazon CloudWatch, allowing you to track the progress of jobs, resource utilization, and other relevant metrics.
Scaling: AWS Batch can automatically scale compute resources based on the workload. It can dynamically adjust the number of instances or containers in the computing environment to accommodate changes in demand.
Key Features of AWS Batch
Flexible Compute Workloads: AWS Batch supports both on-demand and Spot Instances in Amazon EC2, and AWS Fargate for serverless compute environments. This allows you to choose the most cost-effective or high-performance resources based on your workload.
Automatic Job Scheduling: With AWS Batch, job scheduling and queue management are automated, ensuring jobs are executed in the most efficient order.
Dynamic Resource Scaling: AWS Batch dynamically scales compute resources to meet the requirements of your jobs.
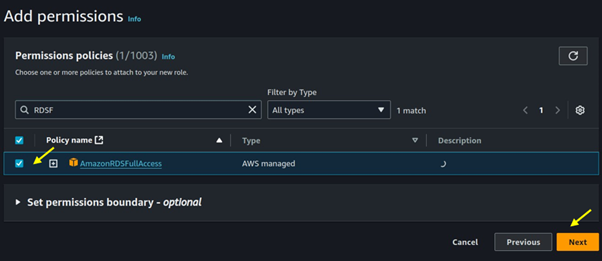
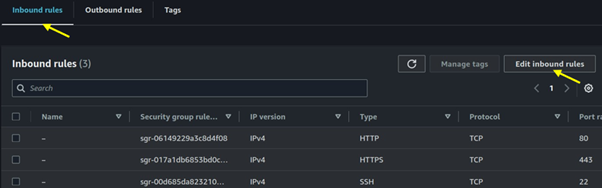
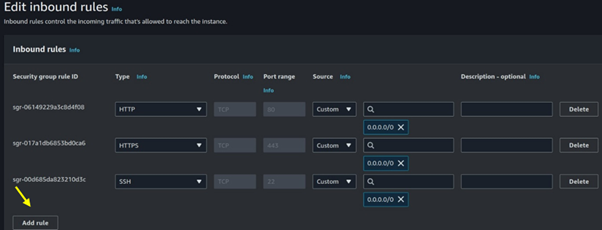
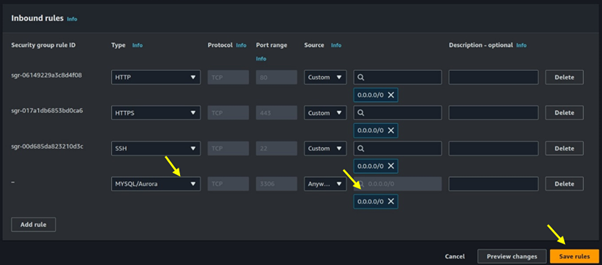
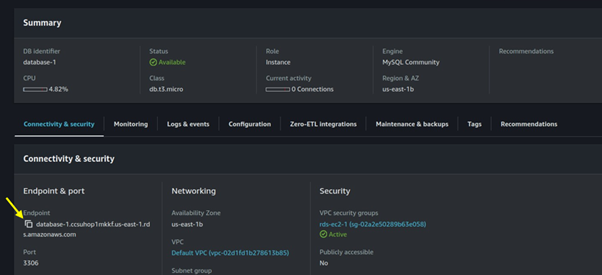
Seamless AWS Integration: AWS Batch integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and Amazon CloudWatch.
Benefits of AWS Batch
- Efficient Job Processing
- Cost-Effective Batch Processing with AWS Spot Instances
- High Scalability
- Easy Integration with Data Pipelines
AWS Batch vs. Other Processing Solutions
When compared to other solutions like Amazon Lambda, Amazon EC2, or traditional on-premises processing, AWS Batch stands out in several ways:
AWS Batch vs. Lambda: AWS Lambda is ideal for lightweight, short-duration tasks, while AWS Batch is designed for long-running, compute-heavy jobs that require scaling across multiple instances.
AWS Batch vs. EC2: AWS Batch is a more efficient choice than manually managing EC2 instances for batch processing, as it automates scaling and job scheduling, reducing the need for administrative overhead.
Batch Processing vs. Real-Time Processing: While AWS Batch excels in handling large-scale, time-independent jobs, real-time processing solutions like AWS Kinesis are better for streaming data and instant analytics.
Common Use Cases for AWS Batch
Data Processing: AWS Batch is ideal for data-intensive tasks such as ETL processes, analytics, and report generation, where jobs are scheduled to process large datasets.
Financial Modeling and Simulations: Financial institutions use AWS Batch for tasks like Monte Carlo simulations, risk assessment, and financial forecasting, which require substantial computing power.
Scientific Research and Analysis: Researchers rely on AWS Batch for simulations, data analysis, and processing large datasets from experiments, which often need parallel computing.
Machine Learning: Data preprocessing for machine learning workflows, such as image processing or data transformation, can be automated and scaled using AWS Batch.
Conclusion
AWS Batch offers a flexible and cost-effective way to manage large computing tasks. It automatically schedules, adjusts, and manages computing resources, making it simpler to handle complex jobs and reducing the need for manual management.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!