Cisco Umbrella
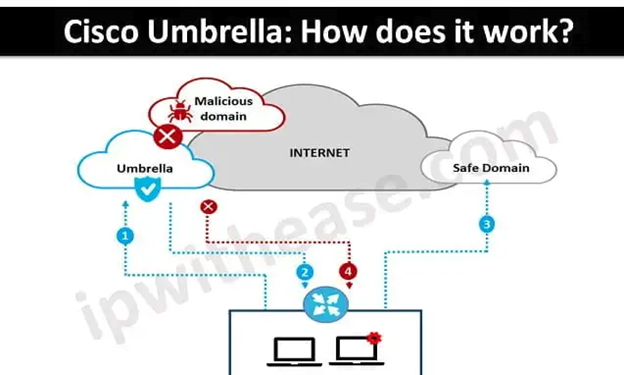
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the need for robust security measures is more critical than ever. Cisco Umbrella, a cloud-delivered security service, is one of the leading solutions in providing secure internet access and controlling cloud app usage from your network, branch offices, and roaming users. This article delves into the configuration of Cisco Umbrella, ensuring your organization remains protected against cyber threats.
Understanding Cisco Umbrella
Cisco Umbrella offers a range of security functionalities, including secure web gateways, DNS-layer security, firewall, and cloud access security broker (CASB) capabilities. It blocks malware, phishing, and command-and-control callbacks over any port or protocol, preventing potential attacks before they even occur.
Components of Cisco Umbrella
Before diving into policy configuration, it’s crucial to understand the key components of Cisco Umbrella:
- DNS Security: Umbrella uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to block malicious domains before a connection is ever established.
- Secure Web Gateway (SWG): Provides deeper inspection of web traffic to prevent malware from being downloaded or data from being exfiltrated.
- Cloud-Delivered Firewall: Manages and enforces application, URL, and IP-based policies to restrict inappropriate access.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): Offers visibility and control over the use of sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services.
- API Integrations: Integrates with other security solutions to provide comprehensive protection.
Configuring Cisco Umbrella Policies
Configuring policies in Cisco Umbrella involves setting rules that dictate how traffic is handled. These policies help in controlling access to malicious sites, enforcing acceptable use policies, and securing sensitive data. Here’s a step-by-step guide to configuring these policies:
- Accessing the Umbrella Dashboard:
- Log in to your Cisco Umbrella account.
- Navigate to the Dashboard, where you can manage and configure your policies.
- Creating Policy Sets:
- Go to the Policies section and select Policy Components.
- Click on Create New Policy Set. Name your policy set to reflect its purpose, such as “Corporate Office” or “Remote Workers.”
- Defining Policy Rules:
- Within the policy set, you can define specific rules based on your organization’s needs.
- Security Settings: Enable DNS-layer security to block malicious domains and prevent malware, phishing, and command-and-control callbacks.
- Content Filtering: Use content categories to block access to inappropriate or non-work-related websites. For example, you can restrict access to social media, gambling, or adult content.
- Application Settings: Control access to cloud applications using the CASB feature. You can define which applications are allowed, monitored, or blocked.
- Setting Up SafeSearch and YouTube Restrictions:
- Under the Content Filtering section, enable SafeSearch to ensure inappropriate content is filtered out from search engine results.
- Enable YouTube Restricted Mode to prevent users from viewing adult or inappropriate content on YouTube.
- Configuring Firewall Policies:
- Navigate to the Firewall section.
- Create rules to control traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols. This helps in blocking unwanted or potentially harmful traffic.
- Applying the Policy:
- Once the policy set is configured, apply it to specific networks, user groups, or devices.
- Use the Identity Management section to assign policies to different user identities, such as Active Directory users, network devices, or roaming clients.
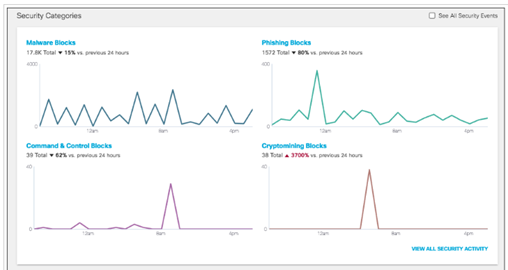
- Monitoring and Reporting:
- Cisco Umbrella provides comprehensive reporting tools. Regularly monitor these reports to understand the effectiveness of your policies and to make necessary adjustments.
- Use the Reports section to view details on blocked requests, security threats, and overall internet activity within your organization.
- Monitoring can also be found right at the main Dashboard screen, see below for an example:
Best Practices for Policy Configuration
- Regularly Update Policies: Cyber threats evolve, and so should your policies. Regularly review and update your policies to address new risks and vulnerabilities.
- User Education: Educate users about the importance of these policies and the role they play in maintaining organizational security.
- Leverage Integrations: Integrate Cisco Umbrella with other security tools for a more comprehensive defense strategy.
- Test Policies: Before applying new policies organization-wide, test them in a controlled environment to ensure they don’t disrupt business operations.
Conclusion
Configuring Cisco Umbrella is essential for maintaining a secure and resilient IT environment. By understanding the various components and carefully setting up policies, organizations can effectively protect against a wide range of cyber threats. Regular monitoring and updates ensure that these protections remain robust in the face of evolving challenges, providing peace of mind and a secure digital experience for all users.
If you have any questions concerning this article or would like for us to assist you with your Cisco Umbrella installation and configuration, please reach out to us by emailing us at sales@accendnetworks.com or call us at 415-408-6111 and we can have an initial discovery call to discuss your requirements.