How to Configure AWS CLI: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners

The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI)is a powerful tool that allows developers and system administrators to manage their AWS services directly from the command line. This blog will walk you through the process of configuring AWS effectively, providing you with the knowledge and best practices to make the most of this essential tool.
What is AWS CLI?
The AWS CLI is a unified tool that provides a consistent interface for interacting with AWS services. With the AWS CLI, you can automate tasks, manage resources, and execute commands without having to navigate through the AWS Management Console.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up AWS CLI
Step 1: Install AWS CLI
Below are step-by-step instructions to configure the AWS CLI on your local machine or an EC2 instance and run multiple commands:
Make sure you have an Instance running, you can as well do this on your local machine.
Install AWS CLI
Ensure that you have the AWS CLI installed on your local machine. You can download and install it from the official AWS CLI download page.
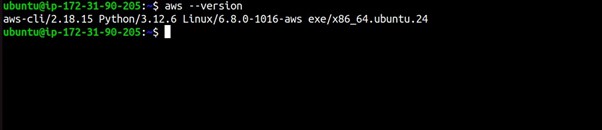
Step 2: Open a Terminal or Command Prompt
Open your terminal.
In the terminal, run the following command:
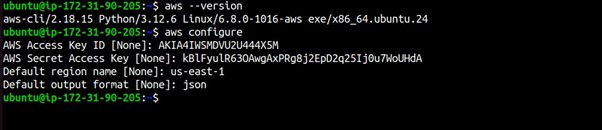
aws configure
Enter AWS Access Key ID
Enter the AWS Access Key ID associated with your IAM user.
Enter the AWS Secret Access Key
Enter the AWS Secret Access Key associated with your IAM user.
Set Default Region
Enter the default region you want to use.
Set Output Format
Choose the default output format.
Example Interaction:
AWS Access Key ID [None]: YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: YOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
Default region name [None]: us-central-1
Default output format [None]: json
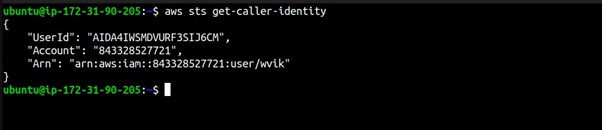
To ensure that your AWS CLI configuration is set up correctly, you can run a simple command to check your credentials:
aws sts get-caller-identity
This command should return details about your AWS account and confirm that your CLI is configured correctly.
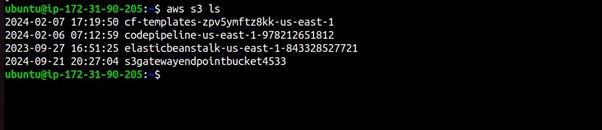
Run AWS CLI Commands
Example 1: List S3 Buckets
aws s3 ls
This command will list the S3 buckets in your AWS account.
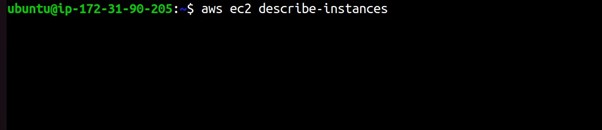
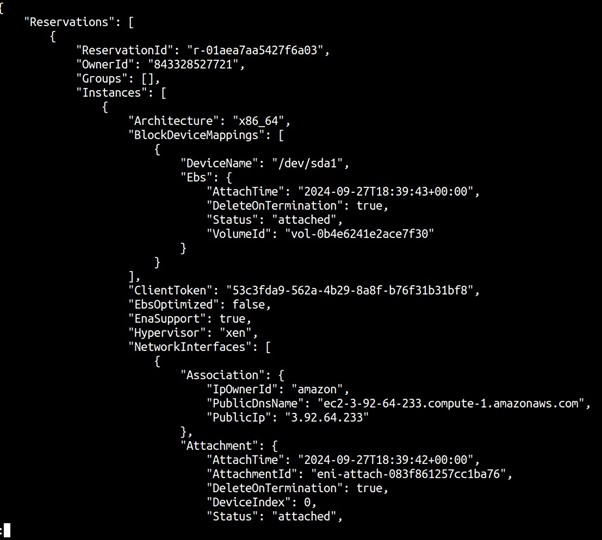
Example 2: Describe EC2 Instances
aws ec2 describe-instances
This command will describe your EC2 instances in the default region.
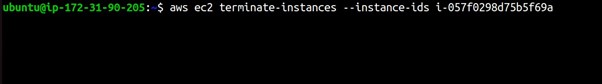
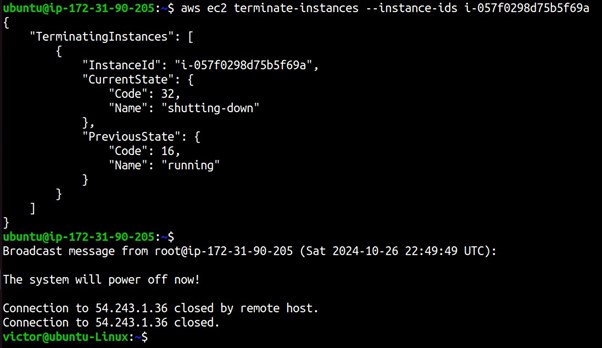
You can also run the CLI command to terminate your EC2 instance as shown below.
Best Practices for Configuring AWS Command Line Interface
Use IAM Roles: Instead of using long-term access keys, consider using IAM roles for enhanced security, especially if you’re running CLI commands from EC2 instances.
Utilize Profiles: If you manage multiple AWS accounts, create separate profiles for each account by using the –profile flag during configuration:
Copy code
aws configure –profile myprofile
Environment Variables: You can also set environment variables for your AWS credentials. This is useful for CI/CD pipelines or automation scripts.
Troubleshooting AWS CLI Configuration Issues
If you encounter issues while using AWS CLI, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
Check Credentials: Ensure that your AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key are correct and have the necessary permissions.
Validate Region: Make sure that the region specified in your configuration is correct and that the services you are trying to access are available in that region.
Session Expiry: If you’re using temporary credentials, be aware that they expire after a certain duration. Refresh your credentials if necessary.
Conclusion
Configuring AWS CLI is a straightforward process that empowers you to manage AWS services efficiently from the command line. By following this step-by-step guide, you can set up AWS CLI, verify your configuration, and implement best practices to enhance your cloud management capabilities.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more.
If you have any questions concerning this article or have an AWS project that requires our assistance, please reach out to us by leaving a comment below or email us at sales@accendnetworks.com.
Thank you!